Anti-Dengue Virus IgM Detected in Urine
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 20 Feb 2020
Dengue viruses (DENV) are transmitted to humans by infected mosquitoes and the disease, known as dengue, occurs throughout the tropics and subtropics. Dengue diagnostic tests rely on a blood sample taken within two weeks of illness onset.Posted on 20 Feb 2020
Dengue initially presents as an acute febrile illness (AFI) that can be difficult to diagnose clinically and differentiate from other AFIs such as malaria, leptospirosis, influenza, and chikungunya; however, even if dengue is suspected and diagnosed early, a patient’s clinical course and outcome is unpredictable.
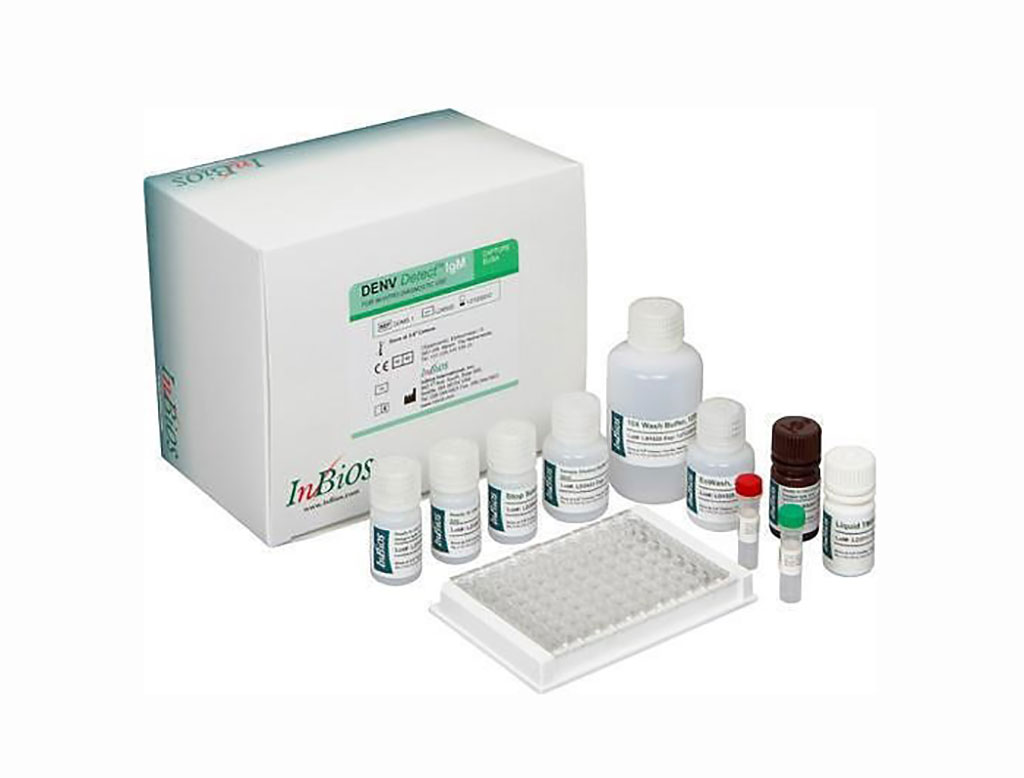
Image: The DENV Detect IgM Capture ELISA is for the qualitative detection of IgM antibodies to DENV recombinant antigens in serum for the presumptive clinical laboratory diagnosis of Dengue virus infection (Photo courtesy of InBios International).
Scientists at the University of Puerto Rico (San Juan, Puerto Rico) and their colleagues used specimens collected from 1,538 study participants enrolled between May 2012-March 2013, of an AFI study conducted in Ponce, Puerto Rico. Study participants with fever for ≤7 days were enrolled, a medical history was obtained, and serum and urine specimens were collected.
Serum specimens collected ≤6 days post-illness onset (DPO) were tested by real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR ) to detect DENV nucleic acid as previously described. Serum specimens collected ≥4 DPO were tested for the presence of anti-DENV IgM by DENV Detect IgM ELISA (InBios International, Inc., Seattle, WA, USA). Urine was tested for anti-DENV IgM, and its sensitivity and specificity to detect sera laboratory-positive dengue cases were calculated. The team evaluated if urine anti-DENV IgM positivity early (≤5 days DPO) and late (6–14 DPO) in the clinical course was associated with dengue severity.
The scientists reported that urine anti-DENV IgM sensitivity and specificity were 47.4% and 98.5%, respectively, when compared with serum anti-DENV IgM ELISA results, and 29.7% and 91.1% when compared with serum rRT-PCR results. There was no correlation between urine anti-DENV IgM positivity and patient sex or pre-existing chronic disease. Early in the clinical course, a significantly higher proportion of those who developed dengue with warning signs had anti-DENV IgM in their urine when compared to those without warning signs (20.4% versus 4.3%). There was no difference in the proportion with urine anti-DENV IgM positivity between severity groups late in the clinical course.
The authors concluded that the use of urine as a surrogate specimen for dengue diagnosis was not sensitive in comparison to serum; however, the presence of anti-DENV IgM urine was highly specific. They were able to identify the presence of anti-DENV IgM in urine specimens from laboratory-positive dengue cases using a simple diagnostic assay. This assay may prove to be useful as a diagnostic tool as well as a prognostic tool to differentiate dengue from dengue with warning signs early in the course of illness (DPO<5). The study was published on January 29, 2020 in the journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
University of Puerto Rico
InBios International