Strongyloidiasis Antibodies Found in Transplant Donors
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 10 Dec 2018
Strongyloidiasis is a neglected tropical disease caused by a parasite, which is endemic in most parts of the world. It can cause a life-threatening disease among immunosuppressed individuals and can be transmitted from solid organ transplant (SOT) donors to recipients.Posted on 10 Dec 2018
Due to the characteristic life cycle of Strongyloides stercoralis, individuals can carry the infection lifelong with mild or no symptoms, unless treated. The disease endemic in large parts of Latin America, Asia and Africa with an estimated prevalence of more than 400 million infected.
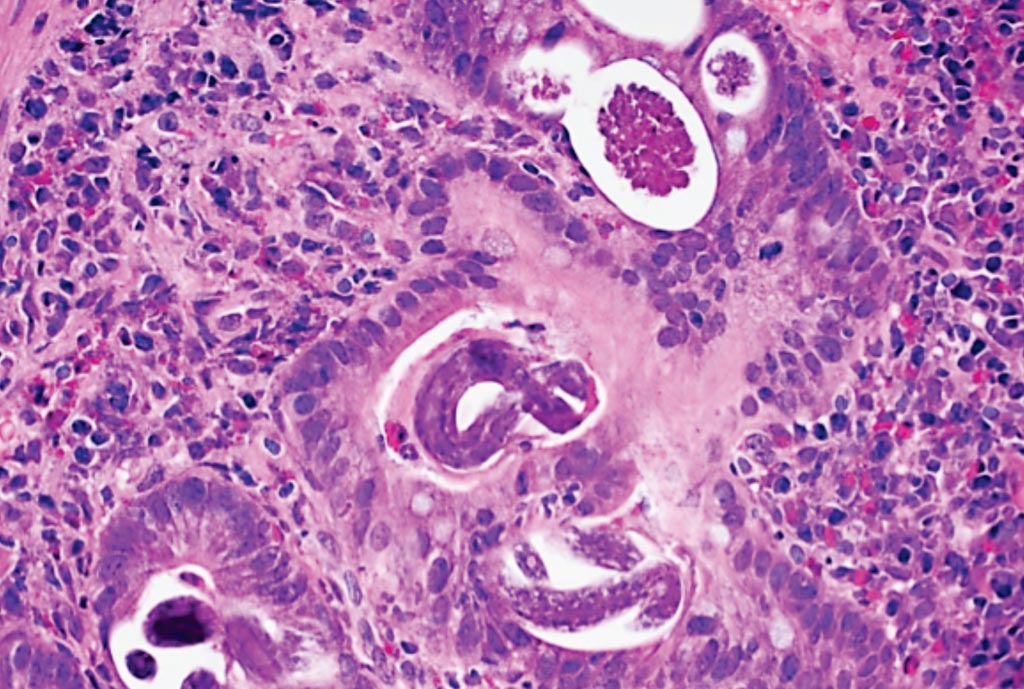
Image: A histopathology of Strongyloides stercoralis in the duodenum (Photo courtesy of Dr. Raul S. Gonzalez, MD).
Scientists at the Universitat de Barcelona (Barcelona, Spain) carried out a retrospective study including all deceased individuals from endemic areas for strongyloidiasis who were considered for organ donation between January 2004 and December 2014 in the Hospital Clinic. During the period 2004–2014, 1,025 deceased individuals were evaluated as potential deceased organ donors. Of these, 90 donors (8.78%) were native from endemic areas for strongyloidiasis. Most were males (63/90 cases; 70%) and median age of all cases was 41 years old. More than half of the deceased organ donors from endemic areas had been born in Latin America (49/90 cases; 54.44%), whereas the rest were from Southeast Asia (24/90 cases; 26.67%) and Africa (17/90 cases; 18.89%).
The team used the serum samples of potential donors from endemic areas for strongyloidiasis, and performed a S. stercoralis serological test. The commercial test IVD-ELISA, which detects immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies by using somatic antigens from larvae of the parasite, was used and has a sensitivity of 91.2%, and a specificity of 99.1%. Currently, IVD-ELISA is the available test in the hospital. The sample is defined as positive if the absorbance/0.2 (i) > 1.1.
The scientists found there were only in 65 of 90 cases available serum samples and analyzed for S. stercoralis serology and 6/65 cases (9.23%) were found to have a positive test for strongyloidiasis. S. stercoralis serology indices ranged between 1.84 and 9.32. From the six positive cases, three individuals were native from Latin America (two from Brazil and one from Ecuador), two from Africa (Senegal and Ghana) and one from Southeast Asia (Philippines).
The authors concluded that they had found a high seroprevalence of strongyloidiasis in individuals from endemic settings evaluated as potential deceased donors for SOT. The data reinforce the importance of following current guidelines recommending systematic screening of potential donors from endemic areas. There is an urgent need to develop rapid diagnostic tests, which can be used in daily clinical practice. The study was published on November 29, 2018, in the journal Public Library of Science Neglected tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
Universitat de Barcelona













