Malaria Diagnosis Employs Hydrophilic-Treated Plastic Plates
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 30 Aug 2017
Malaria is a red blood cell (RBC) infection caused by Plasmodium parasite and to determine RBC infection rate, which is essential for malaria study and diagnosis, microscopic evaluation of Giemsa-stained thin blood smears on glass slides is performed.Posted on 30 Aug 2017
However, only a small area of the blood smear provides a monolayer of RBCs suitable for determination of infection rate, which is one of the major reasons for the low parasite detection rate by Giemsa microscopy. In addition, because Giemsa microscopy is exacting and time-consuming, automated counting of infection rates is highly desirable.
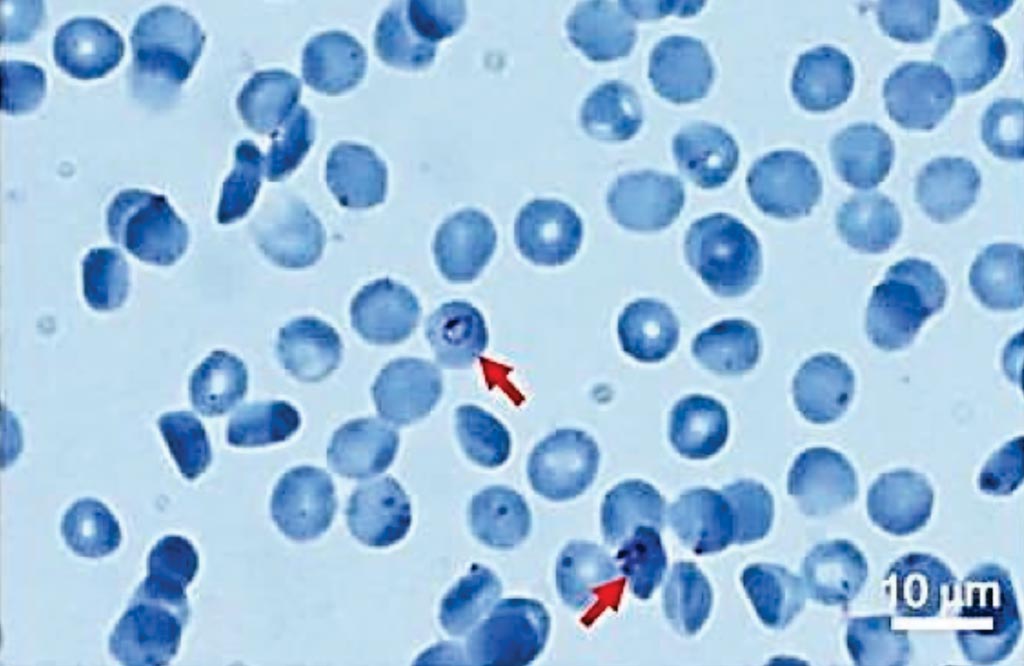
Image: A representative picture of Giemsa-stained hydrophilic-treated COC plates; Arrows indicate Plasmodium-infected cells (Photo courtesy of National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology).
Scientists at the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology (AIST, Tokyo, Japan) cultured a strain of P. falciparum for automated counting of infected parasites; the parasite-infected RBCs were stained with a cell-permeant green fluorescent nucleic acid stain. Bright field and fluorescence images of stained parasite-infected RBCs were acquired using a DM1L inverted fluorescence microscope.
The investigators developed a method that allows for microscopic examination of Giemsa-stained cells spread in a monolayer on almost the whole surface of hydrophilic-treated cyclic olefin copolymer (COC) plates. Because wide-range Giemsa microscopy can be performed on a hydrophilic-treated plate, the method may enable more reliable diagnosis of malaria in patients with low parasitemia burden. Furthermore, the number of RBCs and parasites stained with a fluorescent nuclear staining dye could be counted automatically with a software tool, without Giemsa staining. As a result, medical personnel studying malaria may calculate the infection rate easily, rapidly, and accurately even in low parasitemia.
The authors concluded that because the running cost of these methods is very low and they do not involve complicated techniques, and the use of hydrophilic COC plates may contribute to improved and more accurate diagnosis of malaria. The study was published on August 8, 2017, in the Malaria Journal.
Related Links:
National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology













