Urinary Lipoarabinomannan Assay Screens for Active Tuberculosis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 29 Nov 2016
Symptom-based screening misses approximately one-quarter of active tuberculosis (TB) cases among human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-infected adults, and a more recent study suggested this might be as high as 76% of active TB cases in western South Africa.Posted on 29 Nov 2016
A rapid urine lateral flow assay to detect lipoarabinomannan (LAM), a glycolipid released from the cell wall of TB, has been shown to reduce mortality among HIV-infected hospitalized patients with TB-related symptoms when used to guide anti-TB treatment.
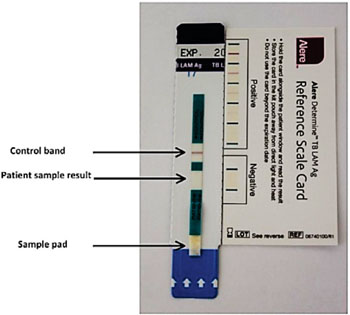
Image: The Determine TB LAM Ag test is targeted for the most vulnerable and hard to diagnose patients (Photo courtesy of Alere).
A team of scientists led by those at the University of Washington (Seattle, WA, USA) conducted a prospective, clinic-based study enrolling consecutive antiretroviral therapy (ART)-naïve HIV-infected adults in the ambulatory clinical areas of two hospitals and two municipal health centers in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa from October 2011 to January 2014. They assessed TB-related symptoms (cough, fever, night sweats, weight loss), and obtained sputum specimens for mycobacterial culture.
Specially trained study nurses tested urine samples for LAM using the Determine TB LAM assay (Alere Inc, Waltham, MA, USA), and interpreted results after 25 minutes. Sputum samples were processed and inoculated into Bactec 960 mycobacterial growth indicator tubes (MGIT; BD, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA), and solid culture Middlebrook 7H11 agar medium. Mycobacterium tuberculosis was confirmed using niacin and nitrate testing.
The investigators found that among 675 HIV-infected adults with median CD4 of 213/mm3 (interquartile range 85-360/mm3), 123 (18%) had culture-confirmed pulmonary TB. They reported that including the LAM assay improved sensitivity to 83%; and NPV to 91% while decreasing the negative likelihood ratio (0.45 versus 0.57). Among participants with CD4 of less than 100/mm3, including urine LAM testing improved the negative predictive value of symptom based screening from 83% to 87%. All screening algorithms with urine LAM performed better among participants with CD4 less than 100/mm3, compared to those with CD4 equal to or more than 100/mm3.
The authors concluded that their results demonstrate a marginal benefit from the inclusion of rapid urine LAM screening to clinical symptom screening among ART-naïve HIV-infected adults in resource-constrained TB-endemic regions. The current urine LAM assay is imperfect and does not solve the public health challenge of screening or diagnosing TB. However, since the principles behind the urine LAM assay are sound, an improved, next-generation urinary LAM assay could meet the criteria for a rapid, clinic-based TB screening test among HIV-infected adults in TB-endemic settings. The study was published on November 14, 2016, in the journal BMC Pulmonary Medicine.
Related Links:
University of Washington
Alere
BD














