Hookworm Egg Detection Methods Compared
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 08 Jan 2015
Microscopy-based identification of eggs in stool offers simple, reliable and economical options for assessing the prevalence and intensity of hookworm infections, and for monitoring the success of helminth control programs. Posted on 08 Jan 2015
An international team of scientists led by those at the University of Copenhagen (Denmark) conducted a study to evaluate and compare the diagnostic parameters of the Kato-Katz (KK) and simple sodium nitrate flotation technique (SNF) in terms of detection and quantification of hookworm eggs. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was used as an additional reference test in stools collected as part of a baseline cross-sectional study in Cambodia.
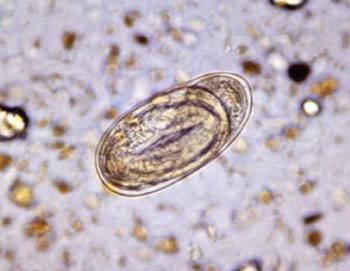
Image: Photomicrograph of an embryonated egg in a stool sample, which is indistinguishable between the Ancylostoma duodenale or Necator americanus hookworm (Photo courtesy of the CDC - US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention).
Fecal samples were collected from 205 people in a Cambodian village and subjected to KK, SNF and PCR for the detection, and in case of microscopy-based methods, quantification of hookworm eggs in stool. For each stool sample two KK smears were prepared and filtered through Number 120-sized nylon mesh screen and a standard plastic KK template was used to deliver 41.7 mg of stool from each sample onto each slide. The SNF was performed using a sodium nitrate solution, centrifugation and a cover-slip which was later mounted on a slide. Genomic DNA was extracted directly from human fecal samples using the PowerSoil DNA Kit (MO BIO Laboratories; Carlsbad, CA, USA) and the PCR products were visualized on 1% agarose gels.
The prevalence of hookworm detected using a combination of three techniques, the gold standard, was 61.0%. PCR displayed a highest sensitivity for hookworm detection at 92.0% followed by 44.0% for SNF, and 36.0% and quadruple KK smears compared to the gold standard. The overall eggs per gram feces from SNF tended to be higher than for quadruple KK and the SNF proved superior for detecting low egg burdens.
The authors concluded that as a reference, PCR demonstrated the higher sensitivity compared to SNF and the quadruple KK method for the detection of hookworm in human stool. For microscopic-based quantification, a single SNF proved superior to the quadruple KK for the detection of hookworm eggs in stool, in particular for low egg burdens. In addition, the SNF is cost-effective and easily accessible in resource poor countries. The study was published on December 18, 2014, in the journal Public Library of Science Neglected Tropical Diseases.
Related Links:
University of Copenhagen
MO BIO Laboratories