PCR-RFLP Distinguishes Between Co-Endemic New World Leishmania Species
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 09 Sep 2014
In a study of clinical samples from patients in southeast Mexico, a PCR-RFLP assay was effective in differentiating between co-endemic species of Leishmania—enabling more fine-tuned diagnoses and more appropriate treatments for patients in a given population with different forms of American (New World) leishmaniasis.Posted on 09 Sep 2014
American cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL) includes: localized CL (LCL) caused by L. (L.) mexicana; diffuse CL (DCL) caused by L. (L.) amazonensis, Leishmania (L.) venezuelensis, and Leishmania (L.) pifanoi; and mucosal CL (MCL) caused by members of the L. braziliensis complex. In endemic regions, multiple species of Leishmania may coexist. Identification of the infecting species based on clinical symptoms is difficult, especially since several species can cause both LCL and MCL. Diagnostic confirmation and correct identification are important for appropriate species-specific therapeutics as well as epidemiologic studies.
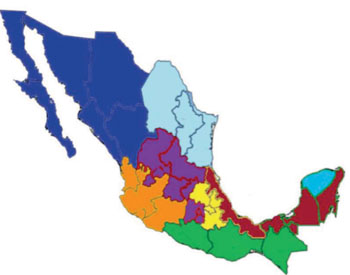
Image: Map of Mexico with Leishmania endemic regions studied shown in maroon coloring – from left to right the states: Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, and Quintana Roo (Photo courtesy of Prof. Monroy-Ostria A. et al., the Instituto Politecnico Nacional, and the journal Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Diseases).
In an international collaboration led by Amalia Monroy-Ostria, professor at the Escuela Nacional de Ciencias Biológicas of the Instituto Politecnico Nacional (IPN; Mexico City, Mexico), a PCR-RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) assay based on the conserved ITS1 (internal transcribed spacer 1) genes was evaluated for direct diagnosis of leishmaniasis and identification of parasite species that, to small but significant extent, coexist in Leishmania-endemic regions of southeast Mexico. Most clinical samples examined, 109/116 (94%), gave patterns similar to L. mexicana, 2 gave patterns similar to L. braziliensis, and 5 gave patterns that suggest a co-infection of 2 strains: co-infection of L. (L.) mexicana and L. (V.) braziliensis or of L. (L.) mexicana and L. (L.) amazonensis. Of 21 Leishmania isolates, 52% displayed a pattern similar to the L. (L.) mexicana strain, 5% showed a mixed pattern compatible with L. (L.) mexicana and L. (V.) braziliensis, 8 with L. (L.) amazonensis and L. (L.) mexicana, and 1 to L. (V.) braziliensis.
The ITS1 PCR-RFLP assay enables diagnosis of leishmaniasis directly (without need for parasite isolation from clinical samples) and simultaneous determination of most infecting species of New World Leishmania, in relatively short time and low cost. Improvements can be made, for example, by further tailoring to sequences that may be found to more specifically characterize local Leishmania species for a given region (e.g., with respect to gene sequences amplified in the PCR or to restriction enzymes used for the RFLP).
The study, by Monroy-Ostria A. et al., was published in the journal Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Diseases, July 2014.
Related Links:
Instituto Politecnico Nacional