Peripheral Blood Smear Confirms Leishmaniasis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 05 Mar 2012
Peripheral buffy coat blood smears are a minimally invasive technique to diagnose the presence of the causative agents of visceral leishmaniasis (VL). Posted on 05 Mar 2012
Buffy coat is the portion of blood that contains concentrates of white blood cells, including monocytes and platelets, and a smear can be examined for detection of amastigotes in suspected VL patients.
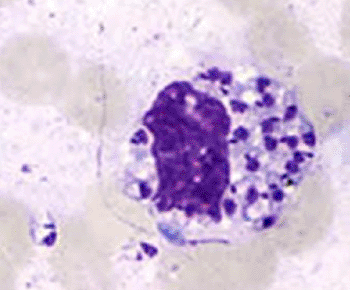
Image: Leishmania amastigotes in stained smear (Photo courtesy of US Centers for Disease Control).
Laboratory staff at Rajshahi Medical College (Bangladesh) enrolled 112 VL patients in a prospective study during June 2009 to June 2010. Splenic aspiration was carried out for 66 patients by an experienced physician. The buffy coat was separated from the other blood components following the principle of concentration gradient separation by using Histopaque solution. Two good-quality smears prepared from buffy coat and stained with Leishman stain were examined under an oil immersion light microscope. Buffy coat DNA was extracted for a nested polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using the QIAamp DNA Blood Mini Kit.
The results of the study showed that 92% (103/112), 95.5% (107/112), and 100% (66/66) of VL patients were positive by buffy coat microscopy, buffy coat PCR, and spleen smear microscopy, respectively. Leishmania amastigotes were found by buffy coat microscopy in 93.5% (100/107) of those positive by buffy coat PCR and in 92.4% (61/66) of those positive for Leishmania amastigotes by spleen smear microscopy. Compared to spleen smear microscopy, the positivity rates of buffy coat PCR and buffy coat microscopy was comparable.
The buffy coat was prepared on Histopaque-1119 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and the DNA extraction kit was from Qiagen (Hilden, Germany) The authors concluded that buffy coat smear was a promising confirmatory diagnostic tool for VL which can be used for point-of-care diagnosis in resource-limited health facilities. Splenic aspiration confirmation is risky and requires skilled personnel, and hence they are unavailable to the poor people in the regions of endemicity. Visceral leishmaniasis or Indian Kala-Azar is a vector-borne parasitic disease caused by an obligate intracellular hemoflagellate of the genus Leishmania and is fatal if it is not adequately treated. There are an estimated 500,000 new cases and 75,000 to 80,000 deaths per year, worldwide. The study was published in March 2012, in the Journal of Clinical Microbiology.
Related Links:
Rajshahi Medical College
Sigma-Aldrich
Qiagen














