AI-Powered Immuno-Oncology Tool Predicts Lung Cancer Treatment Outcomes
Posted on 02 Dec 2024
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI) are used to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) by enhancing the immune system's ability to fight cancer. However, identifying which patients will benefit most from this treatment remains a challenge. Now, advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and diagnostic tools offer the potential to enhance treatment outcomes and survival rates for NSCLC patients by helping doctors more accurately predict their response to ICI therapy.
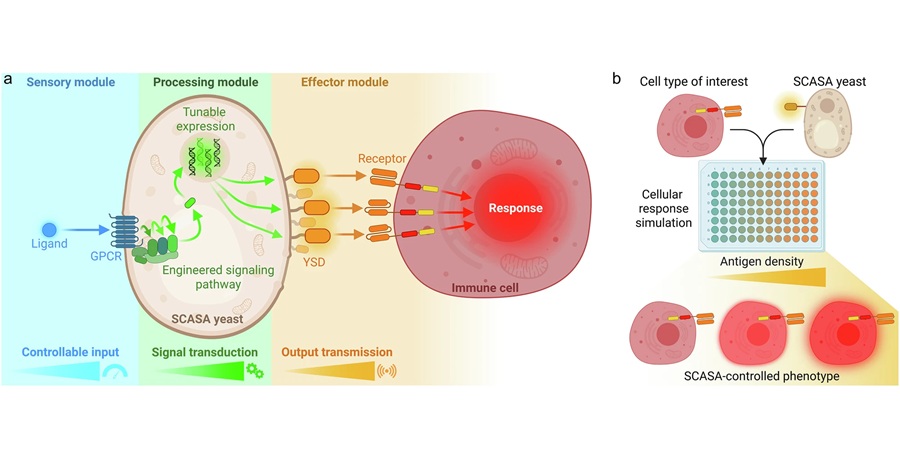
Researchers at SUNY Upstate Medical University (Syracuse, NY, USA) have developed HistoTME, an affordable and easy-to-implement AI tool. This advanced deep learning algorithm analyzes routinely stained histopathology images of tumor samples to predict molecular subtypes (based on bulk RNA sequencing), providing insights into the tumor microenvironment (TME). By examining these pathology images, HistoTME identifies specific cell types in the surrounding tumor tissue, offering valuable information about the patient's unique TME composition. This is crucial for predicting personalized ICI treatment responses, especially in patients with low PD-L1 expression, a key marker commonly used in companion diagnostics. The algorithm was validated on a multi-modal dataset comprising over 650 lung cancer patients and more than 1500 images.
The researchers hope this method will assist doctors in selecting personalized treatment plans with greater accuracy and cost-efficiency, especially for patients without access to expensive molecular testing. Moreover, this test could complement existing companion diagnostics, which often struggle to identify the appropriate patients for the right treatments. The next phase of the study will involve clinical validation of HistoTME, which will further evaluate its effectiveness in real-world clinical environments and may lead to its integration into routine cancer care.
“AI-driven diagnostics and prognostication have the potential to transform the future of healthcare practices and precision oncology,” said Upstate researcher Tamara Jamaspishvili, MD/PhD, who won the "Best Research Poster" Award for Faculty at the Digital Pathology Association's national conference, PathVisions 2024 for her work using AI and computational pathology to improve cancer diagnosis and treatment.