Optical Biosensor Reduces Time for Sepsis Diagnosis
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 12 Feb 2020
New point‐of‐care diagnostic devices are urgently needed for rapid and accurate diagnosis, particularly in the management of life‐threatening infections and sepsis, where immediate treatment is key.Posted on 12 Feb 2020
A novel portable biosensor based on nanoparticle‐enhanced digital plasmonic imaging has been developed for rapid and sensitive detection of two sepsis‐related inflammatory biomarkers, procalcitonin (PCT) and C‐reactive protein (CRP) directly from blood serum.
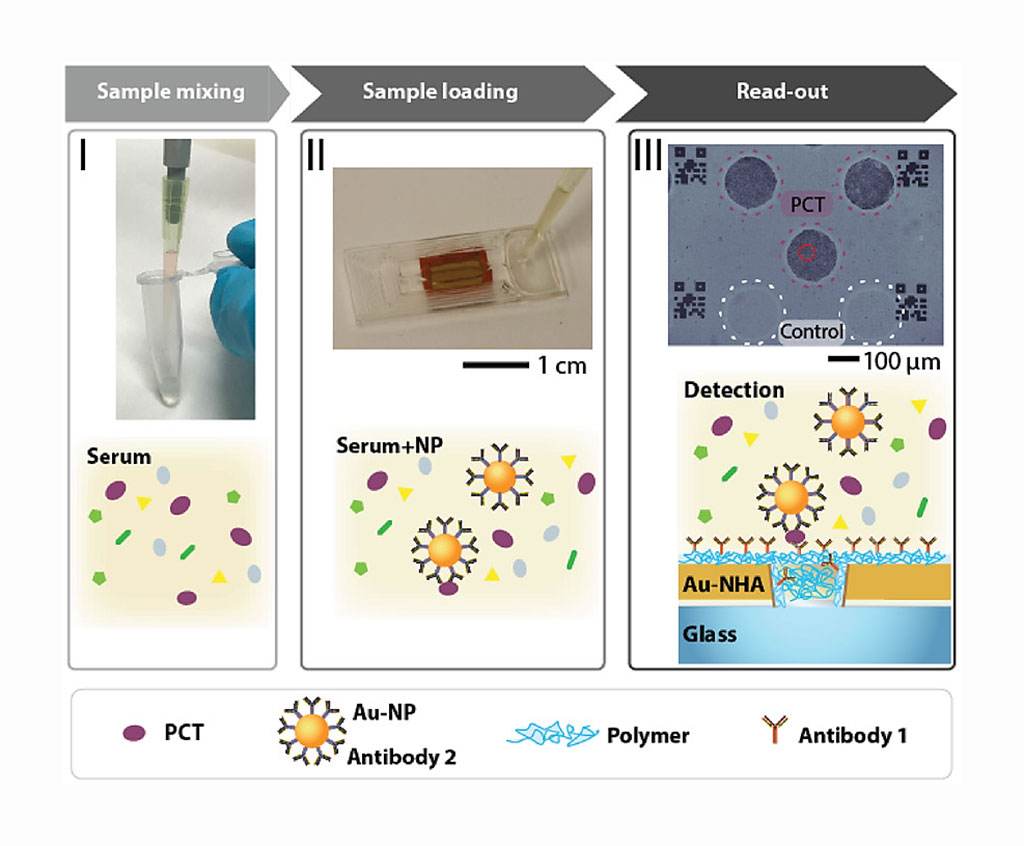
Image: Detection and quantification of procalcitonin and C‐reactive protein using detection of inflammatory biomarkers imager (DENIS) (Photo courtesy of Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne).
Bioengineers from the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (Lausanne, Switzerland) and their colleagues drew on recent developments in nanotechnology and on light effects at a nanoscale to create a highly portable, easy-to-use device that can rapidly detect sepsis biomarkers in a patient's bloodstream, and their device takes just a few minutes to deliver a result, like a pregnancy test.
The device employs an optical metasurface, in this case a thin gold sheet containing arrays of billions of nanoholes. The metasurface concentrates light around the nanoholes so as to allow for exceptionally precise biomarker detection. With this type of metasurface, the team can detect sepsis biomarkers in a blood sample with nothing more than a simple LED and a standard CMOS camera. The team began by adding a solution of special nanoparticles to the sample that are designed to capture the biomarkers and then distribute this mixture on the metasurface.
The generated images are used to rapidly determine whether disease biomarkers are present in a sample and, if so, in what concentration. They used the new device to measure the blood serum levels of two important sepsis relevant biomarkers, PCT and CRP. Doctors can use this information to accelerate the triage of sepsis patients, ultimately saving lives. The device was installed at the Vall d'Hebron University Hospital (Barcelona, Spain) and used in blind tests to examine patient samples from the hospital's sepsis bank.
The authors concluded that portable digital nanoparticle‐enhanced plasmonic imager that enables rapid detection of two inflammatory sepsis‐related biomarkers, PCT and CRP. The unique nanoplasmonic mechanism through imaging of single gold nanoparticles (Au‐NPs) binding on the gold nanohole arrays (Au‐NHAs) enables highly sensitive and rapid biomarker detection directly in blood serum. The compact nanoplasmonic reader, built of inexpensive components, weighs less than 1 kg. The study was published on January 23, 2020 in the journal Small.
Related Links:
Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne
Vall d'Hebron University














