Novel Diagnostic Device Profiles Population of Gut Microbiome
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 05 Aug 2019
Researchers used a three-dimensional (3D) printer to manufacture a novel pill-like diagnostic tool capable of profiling the bacterial species comprising the gut microbiome in the critical area between the stomach and the colon.Posted on 05 Aug 2019
Investigators at Tufts University (Medford/Somerville, MA, USA) recently described a novel non-invasive diagnostic tool capable of providing a profile of microbiome populations throughout the entire GI tract. The device was manufactured in a three-dimensional printer.
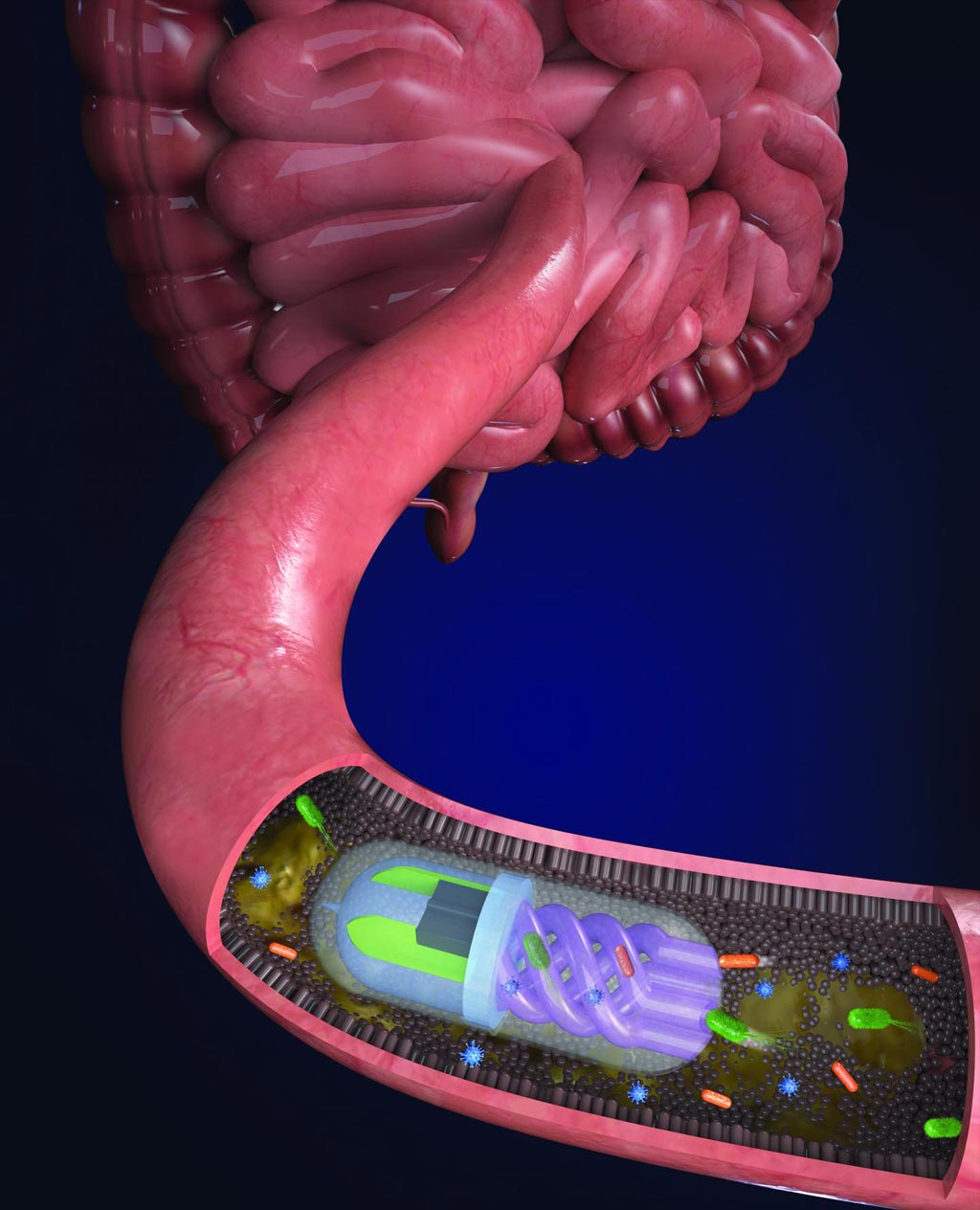
Image: Bacteria in the gut are pulled into the helical channels by an osmotic “pump” generated by a calcium salt-filled chamber within the pill (Photo courtesy of Nano Lab, Tufts University).
The surface of the pill was covered with a pH-sensitive coating, so that it did not absorb any substances until it passed through the stomach and entered the small intestine, where the coating dissolved. A semi-permeable membrane separated two chambers in the pill - one containing helical channels that captured bacteria and the other containing a calcium salt-filled chamber, which created an osmotic flow across the membrane that forced the bacteria into the helical channels. A small magnet in the pill enabled controlled movement and targeting via a magnet outside the body. Finally, a fluorescent dye in the salt chamber marked the pill for easy identification after it left the body.
The pill's sampling performance was characterized using realistic in vitro models and validated in vivo in pigs and primates. So far, results have indicated that the bacterial populations recovered from the pills’ microfluidic channels closely resembled the bacterial population demographics of the microenvironment to which the pill was exposed. Despite these promising results, clinical trials will be needed to determine if the pill can be adapted for routine use in humans.
"We are learning quite a lot about the role of gut microbiome in health and disease. However, we know very little about its biogeography," said senior author Dr. Sameer Sonkusale, professor of electrical and computer engineering at Tufts University. "The pill will improve our understanding of the role of spatial distribution in the microbiome profile to advance novel treatments and therapies for a number of diseases and conditions."
The microbiome profiler was described in the July 19, 2019, online edition of the journal Advanced Intelligent Systems.
Related Links:
Tufts University














