Abnormal Metabolite Observed in Early CKD Patients
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 06 Aug 2019
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) has been a growing health burden worldwide, and the patients with CKD continue to suffer from a wide range of complication including electrolyte imbalance, fluid overload, bone and mineral metabolism disorder to anemia.Posted on 06 Aug 2019
CKD has been recognized as risk factors for 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH) D) deficiency and low levels of 25 (OH) D have been suggested to be a trigger factor of decreased level of hemoglobin. However, there is lack of information about the magnitude of 25(OH) D deficiency and hemoglobin level in Nepalese CKD patients.
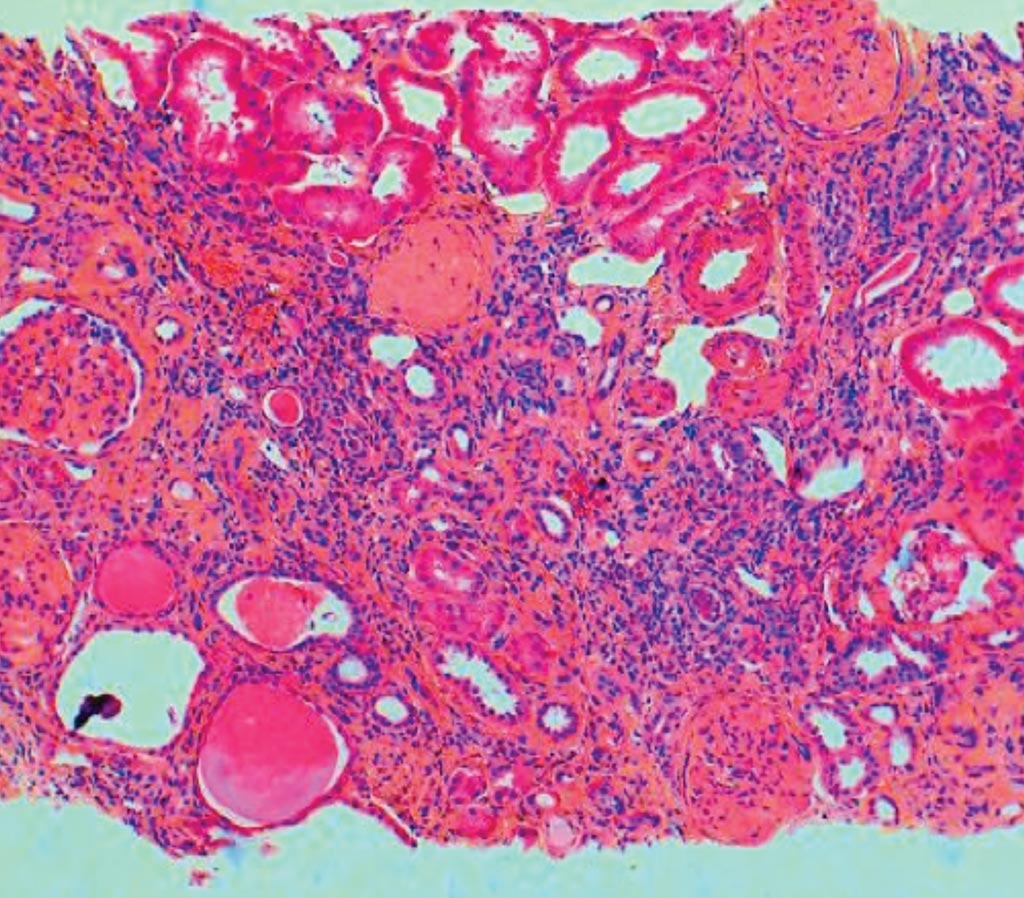
Image: A histopathology of chronic interstitial nephritis in end-stage kidney disease. There is diffuse interstitial scarring with a nonspecific mononuclear infiltrate (Photo courtesy of Agnes B. Fogo MD, Michael Kashgarian MD).
Two Nepalese scientists associated with Purbanchal University (Kathmandu, Nepal) carried out a cross-sectional study was carried out between June 2016 to May 2017 in the patients visiting outpatient nephrology unit at Kathmandu medical and teaching hospital and a total 172 patients who met the inclusion criteria were included in the study. All the patients had had measurement of serum creatinine, 25(OH) D and urine albumin creatinine. Clinically stable and with a diagnosis of CKD stage 2–5 who were not on dialysis were recruited for the study.
The core variables of interest in this study were 25(OH) D level and hemoglobin concentration. The following covariates included in statistical analysis: age, sex, co-morbidities (hypertension, and diabetes), biochemical laboratory test including estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), hemoglobin (Hb), intact parathyroid hormone (iPTH), serum phosphate, albumin, calcium, and phosphate. Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay (ECLIA) test was used to measure the level of 25(OH) D and cyanmethemoglobin method for the estimation of Hb level.
The scientists reported that the estimated prevalence of abnormal 25(OH) D metabolite of less than 30 ng/mL in the predialysis patients were (87.8%), with 32% and 55.8% deficiency and insufficiency 25(OH) D metabolite, respectively. On regression analysis, serum 25(OH) D was positively associated with male subjects, serum albumin, and eGFR, while inversely associated with age, iPTH. Hb concentration was found to be positively correlated with 25(OH) D in both univariate as well as in multivariate analysis.
The authors concluded that Hb concentration significantly, positively correlated with 25(OH) D age, eGFR and calcium level. Conversely, there was inverse relationship between Hb and iPTH. The study shows that lower level of 25(OH) D level are associated with lower level of Hb and higher level of iPTH, and could play a role in the development of anemia and hyperparathyroidism. The study was published on July 17, 2019, in the journal BMC Nephrology.
Related Links:
Purbanchal University














