Levels of IgA Nephropathy Associated with Disease Severity
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 03 Dec 2018
IgA nephropathy (IgAN) is the most common cause of primary glomerulonephritis. IgAN is associated with a poor prognosis, about 20% to 40% of patients with IgAN progress slowly to end-stage renal failure 20 to 25 years after diagnosis.Posted on 03 Dec 2018
Cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) play an important role in aberrant mucosal immune response in the early phase of the pathogenesis in IgAN, and mesangial cell proliferation, hyperproduction of extracellular matrices, podocyte injury and glomerulosclerosis in the second phase.
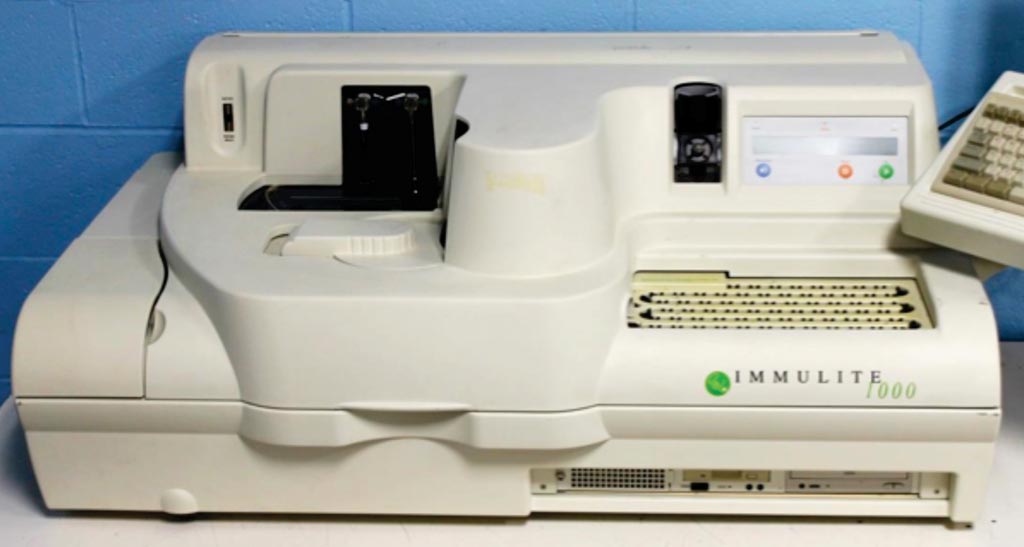

Image: The IMMULITE 1000 system is a small bench top immunoassay analyzer (Photo courtesy of Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics).
Scientists at the Peking Union Medical College Hospital (Beijing, China) collected serum samples were collected from 147 patients with biopsy-proven primary IgAN between July 2016 and April 2017. The patients accepted renal biopsy between November 1999 and December 2016. In addition, 126 serum samples were collected from healthy volunteers who had no known kidney diseases between August 2015 and February 2016.
The serum samples were separated as soon as possible from the clot of red cells after centrifugation to avoid TNF-α production by blood cells that falsely could increase its values. Separated sera were measured immediately. Levels of serum TNF-α were measured using Tumor necrosis factor-alpha Assay Kit (chemiluminescent assay) through IMMULITE 1000 system.
The team reported that serum levels of TNF-α were higher in patients with IgAN, 9.20 (7.7–10.6) pg/mL versus 6.04 (5.11–7.23) pg/mL in healthy subjects. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis revealed that TNF-α had better discrimination between patients with IgAN and healthy controls than estimated glomerular filtration rate. Multivariate linear regression analyses showed that serum levels of TNF-α were positively correlated with 24-hour urine protein excretion, urinary protein to serum creatinine ratio, serum creatinine and Cystatin C in IgAN and negatively correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate after adjustment for sex, systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure. Patients with higher mesangial hypercellularity or tubular atrophy/interstitial fibrosis score according to Oxford classification showed higher serum levels of TNF-α.
The authors concluded that serum levels of TNF-α detected by chemiluminescence immunoassay was a potential biomarker for evaluating the disease severity in IgAN. The study was published on November 14, 2018, in the journal BMC Nephrology.
Related Links:
Peking Union Medical College Hospital