Mast Cell Activation Test Diagnoses Allergic Diseases
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 16 May 2018
Peanut allergies are among the most common food allergies in children. Currently, doctors diagnose peanut allergy using a skin-prick test or immunoglobulin E (IgE) test, but this may result in over-diagnosis or false-positives and it cannot differentiate between sensitivity and true food allergy.Posted on 16 May 2018
When skin-prick and IgE test results are unclear, allergists rely on an oral food challenge (OFC), which consists of feeding peanut in incrementally larger doses to a patient in a highly controlled setting in hospital to confirm allergy to the food. While the test is the gold standard for diagnosing food allergies, there is risk of causing severe allergic reactions.
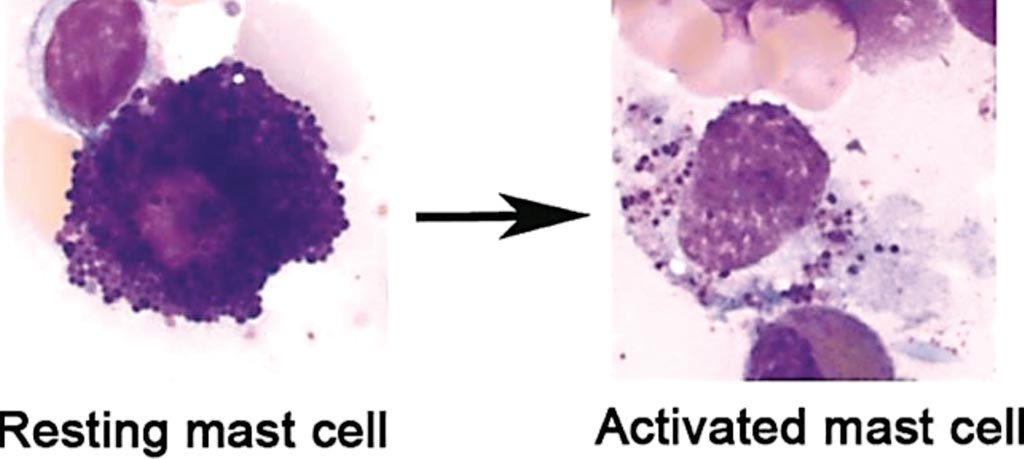
Image: Mast cells obtained from the human bone marrow; May-Grünwald/Giemsa stain of a resting human mast cell and a mast cell following activation-induced degranulation. Note the loss of granule staining (Photo courtesy of University Hospital of Bonn).
Scientists at the University of Manchester (Manchester, UK) and their colleagues have developed a new laboratory test to diagnose peanut allergy. The team used blood samples from 174 children participating in allergy testing, 73 peanut allergic and 101 peanut-tolerant, the scientists added peanut protein to mast cells to screen for IgE-mediated activation. Levels of total IgE, peanut-specific IgE, and IgE to the recombinant allergen components were measured by using ImmunoCAP. Skin prick tests (SPTs) were undertaken according to national guidelines by using lancets and commercial peanut extract, with 1% histamine as a positive control. Images of mast cell activation were collected on an Olympus BX51 upright microscope.
The scientists found that human blood-derived mast cells (MCs) sensitized with sera from patients with peanut, grass pollen, and Hymenoptera (wasp venom) allergy demonstrated allergen-specific and dose-dependent degranulation, as determined based on both expression of surface activation markers (CD63 and CD107a) and functional assays (prostaglandin D2 and β-hexosaminidase release). In this cohort of peanut-sensitized subjects, the mast cell activation test (MAT) was found to have superior discrimination performance compared with other testing modalities, including component-resolved diagnostics and basophil activation tests. They identified five clusters or patterns of reactivity in the resulting dose-response curves, which at preliminary analysis corresponded to the reaction phenotypes seen at challenge.
The authors concluded that the MAT is a robust tool that can confer superior diagnostic performance compared with existing allergy diagnostics and might be useful to explore differences in effector cell function between basophils and MCs during allergic reactions. The study was published on March 5, 2018, in The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
Related Links:
University of Manchester









 Analyzer.jpg)




