Noninvasive Prenatal Test Developed for Sickle Cell Disease Risk
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 01 Aug 2019
Sickle cell disease (SCD) is an autosomal recessive disease, meaning that a child has to inherit two mutated copies of the hemoglobin gene to develop it, one from each parent. If both parents have sickle cell trait, there is a 25% chance the child will have SCD.Posted on 01 Aug 2019
Without early diagnosis and treatment, the life expectancy of children with SCD is only a few years. Currently, sickle cell can only be diagnosed during pregnancy using an invasive test like amniocentesis that carries a risk, although small, of miscarriage, leading some parents to decline it. An earlier survey showed that if patients had the option of a non-invasive test, more would choose screening for the possibility of SCD.
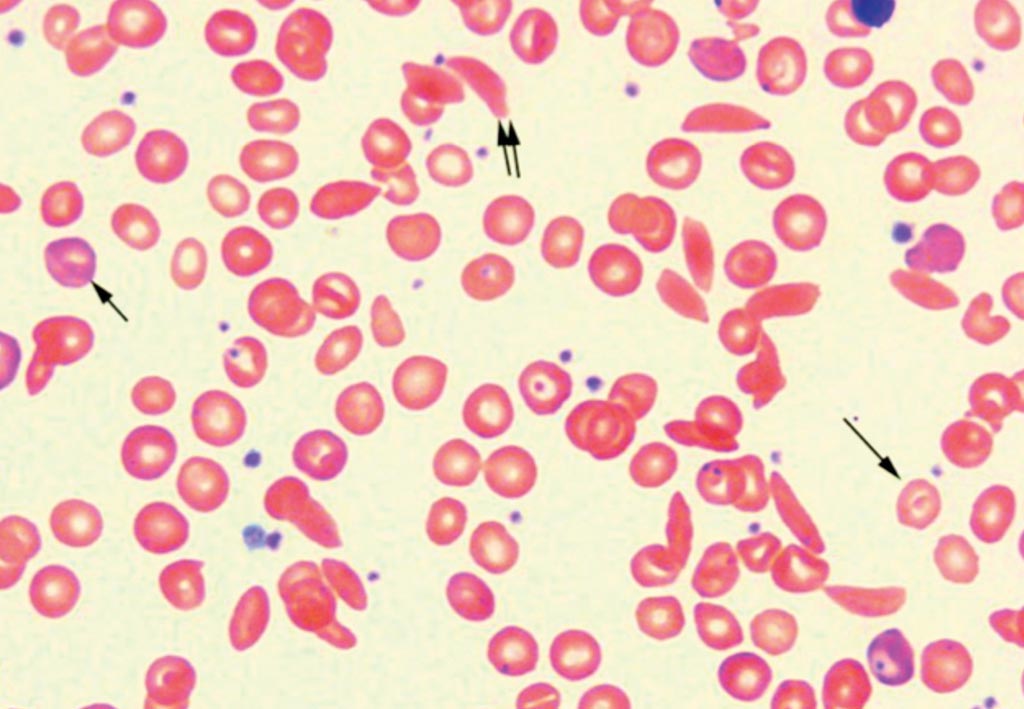
Image: A blood smear of a patient with Sickle Cell Disease. Polychromatophilic reticulocytes are present (small single arrow). Target cell (large single arrow) and sickle cell (double arrow) can be seen in this view (Photo courtesy of John Lazarchick).
A team of scientists working with the Guy's and St. Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust (London, UK) analyzed blood samples from 24 pregnant carrying a mutated copy of the hemoglobin gene, and as such were sickle cell carriers. The scientists optimized their method to enrich the samples for the fetal DNA, and used a molecular barcode to identify the mutant and normal gene. They use targeted next-generation sequencing of cell-free DNA from maternal plasma to diagnose fetal sickle cell disease based on a relative mutation dosage approach. No paternal or proband samples were required. Unique molecular identifiers (UMIs) were incorporated into library preparation to enable accurate quantification of mutant and wildtype allele reads.
When the 24 plasma samples from pregnant sickle cell disease carriers were analyzed, 20 were concordant with the established genotype; two with low fetal fraction were inconclusive and two were discordant. In silico size selection of cell free DNA (cfDNA) fragments was found to enhance the fetal fraction for all samples, and modifications to UMI capture improved diagnostic accuracy. Samples from as early as eight weeks gestation were successfully genotyped.
The authors concluded that they had demonstrated that non-invasive prenatal diagnosis for sickle cell disease is approaching clinical utility. Other autosomal recessive disorders may benefit from a similar approach. Julia van Campen, PhD, a geneticist and the first author of the study, said, “Although cell-free fetal DNA testing is already available for some disorders, technical difficulties have hampered the development of such a test for SCD, despite it being one of the most commonly requested prenatal tests in the UK.” The study was presented at the 2019 European Human Genetics Conference held June 15-18, 2019, in Stockholm, Sweden.
Related Links:
Guy's and St. Thomas' NHS Foundation Trust














