Genetic Changes Linked to Leukemia in Down’s Syndrome Children
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 24 Jul 2019
Of the 30% of children with Down's syndrome who are found to have 'myeloid preleukemia', only 10% of those will go on to develop myeloid leukemia (3% of all children with Down's syndrome). Until now, it was not understood why only some children with the GATA1 mutation were progressing to full leukemia, while others were not.Posted on 24 Jul 2019
The specific gene mutations required for the development of leukemia in children with Down's syndrome have been discovered. Children with Down's syndrome have a 150-fold increased risk of myeloid leukemia, and while some of the genetic causes of this have been previously established, and a new study has identified a wide range of mutations and how they functionally interact to lead to leukemia.
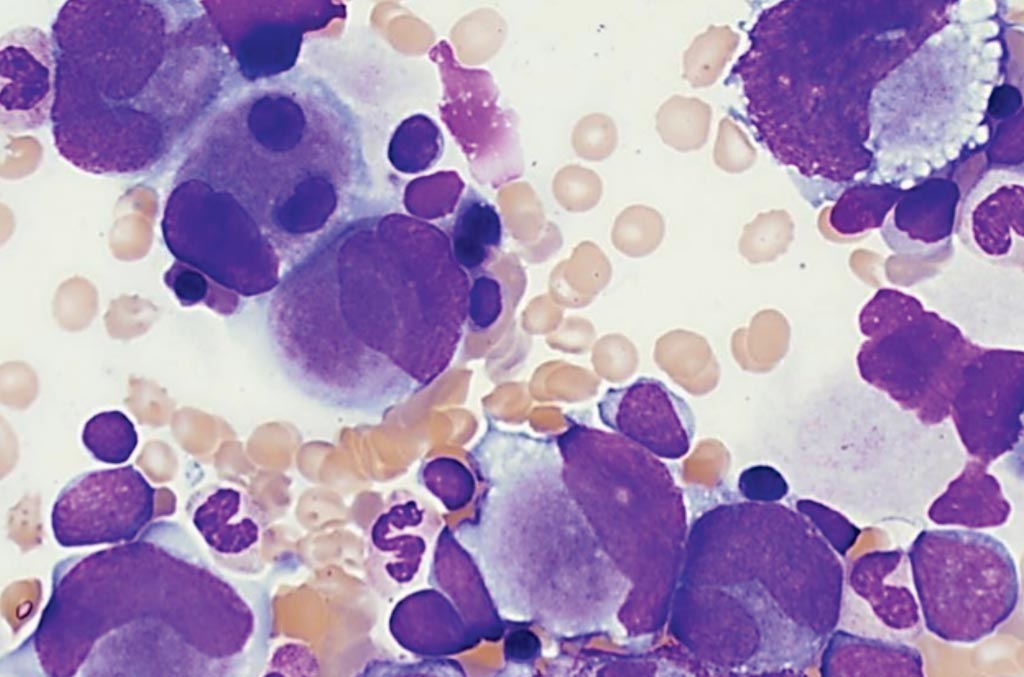
Image: Bone marrow aspirate of a patient with myeloid leukemia associated with Down’s syndrome. The smear includes frequent atypical megakaryocytes. Blasts are increased (11%). As in the peripheral blood, a subset of the blasts has cytoplasmic blebs (Photo courtesy of Elizabeth L. Courville, MD).
An international team of scientists collaborating with those at the University of Oxford (Oxford, UK) combined exome and targeted resequencing of 111 transient abnormal myelopoiesis (TAM) and 141 myeloid leukemia-Downs’s syndrome (ML-DS) samples with functional analyses. TAM requires trisomy 21 and truncating mutations in GATA1; additional TAM variants are usually not pathogenic. By contrast, in ML-DS, clonal and subclonal variants are functionally required.
The scientists identified a recurrent and oncogenic hotspot gain-of-function mutation in myeloid cytokine receptor CSF2RB. By a multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 screen in an in vivo murine TAM model, they tested loss-of-function of 22 recurrently mutated ML-DS genes. Loss of 18 different genes produced leukemias that phenotypically, genetically, and transcriptionally mirrored ML-DS.
Paresh Vyas, MRCP FRCP FRCPath, a Professor of Hematology and a study author, said, “90% of babies with Down's syndrome do not go on to develop preleukemia. But until now, we did not fully understand why some babies did develop leukemia. 'To answer this question, we carefully characterized the mutations in genes required for leukemia to develop. We found that additional genetic changes are required in the altered GATA1 blood cells, and these additional changes transform the preleukemic blood cells into leukemic blood cells.” In total, 43 different altered genes were found. The study was published on July 11, 2019, in the journal Cancer Cell.
Related Links:
University of Oxford








 Analyzer.jpg)





