Parental Screening Can Prevent Hydrops Fetalis in Fetus
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 10 Jan 2018
Hydrops fetalis (fetal hydrops) is a serious fetal condition defined as abnormal accumulation of fluid in two or more fetal compartments, including ascites, pleural effusion, pericardial effusion, and skin edema.Posted on 10 Jan 2018
Fetal anemia is often assumed to be due to red cell alloimmunization and Parvovirus infection, and can lead to hydrops fetalis and death in utero, while other causes, such as mutations of hemoglobin alpha, are less commonly considered.
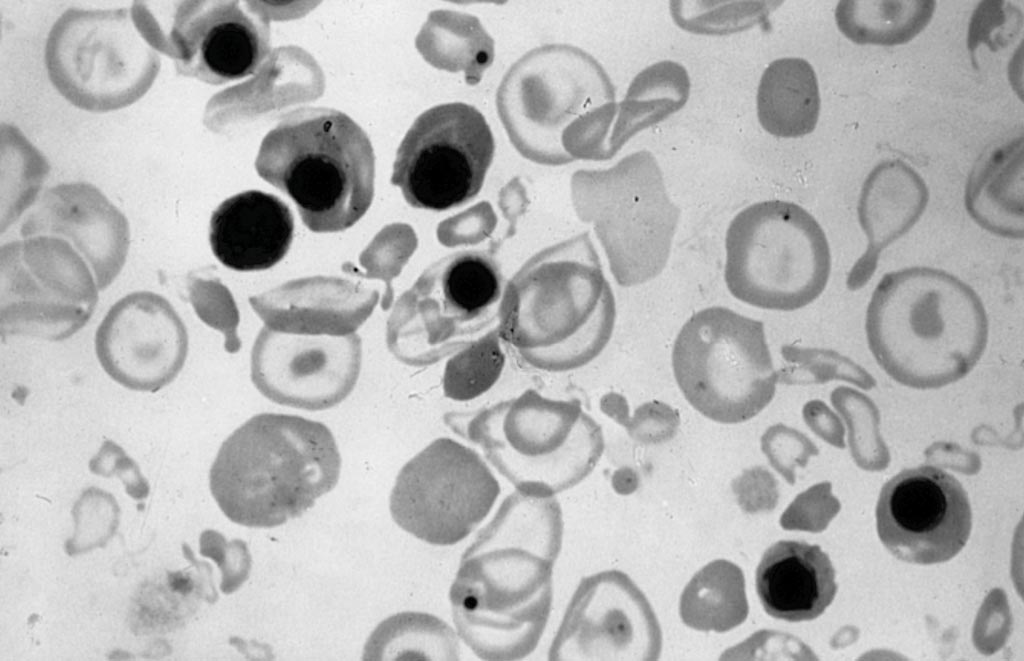
Image: Peripheral blood film from a newborn with hydrops fetalis; note the hypochromia, anisopoikilocytic changes, and erythroblastosis (Photo courtesy of Boston Medical Center).
Hematologists at Khon Kaen University (Khon Kaen, Thailand) reported on report seven cases with fetal anemia causing hydrops fetalis. They performed cordocentesis to find the cause of fetal anemia and check fetal hemoglobin for consideration of intrauterine infusion. Investigations for fetal anemia include complete blood count, blood morphology, and blood group of mother and fetus, reticulocyte counts, red cell indices, screening for thalassemia, hemoglobin typing, acid elution test, parvovirus B 19 serology, and TORCH titer (toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex virus, human immunodeficiency virus, and syphilis).
The seven cases with fetal anemia were prenatally diagnosed from gestational ages 20 to 34 weeks. Initial hematocrit in these cases varied from 9% to 17.2%. In each case, causes of anemia were determined using the investigations listed above. Intrauterine infusion, using irradiated prestorage filtered red cell with hematocrit level of 80%, is indicated if fetal hemoglobin is less than 10 g/dL. All cases underwent uneventfully up to three intrauterine transfusions.
The DNA study for thalassemia demonstrated homozygous Constant Spring (CS) in five cases, homozygous CS with heterozygous E in one case, and compound heterozygous CS and Pakse in one case. The perinatal outcomes were normal term in five cases, preterm in two cases. Low birth weight was determined in two cases. The screening for thalassemia major, including the osmotic fragility and dichlorophenol indophenol precipitation test (DCIP), was not helpful for detecting hemoglobin variants such as Constant Spring or Pakse.
The authors concluded that their study emphasizes homozygous Constant Spring and compound heterozygous CS and Pakse as a cause of hydrops fetalis. Proper management for the fetus after diagnosis can lead to a good fetal outcome. Prevention control programs should include screening of parents for the heterozygous state. The study was published on December 12, 2017, in the Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology.
Related Links:
Khon Kaen University














