Lymphocyte Subtyping Proves Useful in Predicting Pneumonia
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 13 Apr 2017
Pneumocystis jirovecii is an opportunistic fungus that can cause interstitial pneumonia in the immunocompromised host and is associated with a high mortality rate. Antimicrobial prophylaxis reduces the occurrence of P. jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) considerably in susceptible patients.Posted on 13 Apr 2017
Clinical guidelines for PCP prophylaxis exist for patients who are human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-positive, transplant recipients, and those who have hematological malignancies requiring T-cell depleting agents. In other populations, such as those with inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, no consensus recommendation is available to determine who should receive prophylaxis.
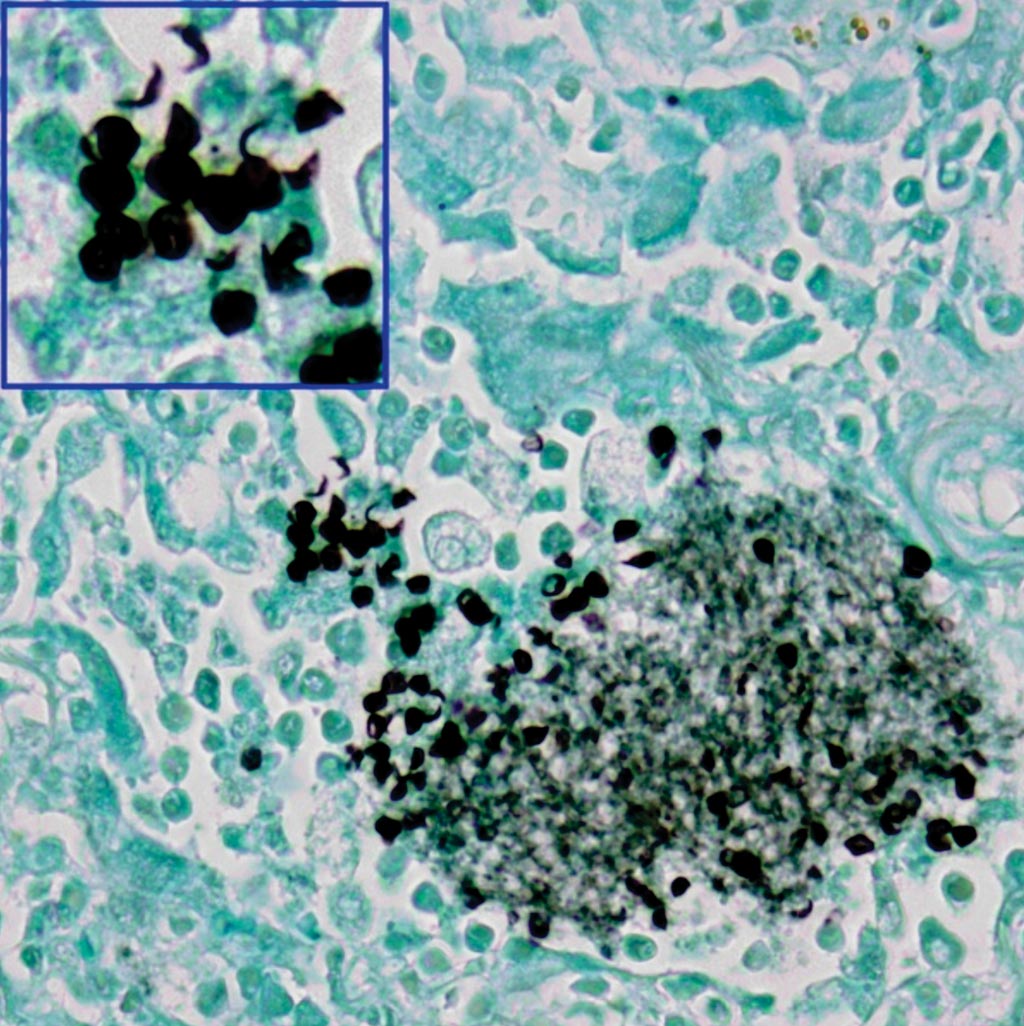
Image: A photomicrograph of lung tissue stained with Grocott-Gomori methenamine silver nitrate. Pneumocystis jirovecii organisms are highlighted as black, disc-like entities within the alveolar cast (Photo courtesy of SPL).
Scientists at the University of Montreal and their Chinese colleagues performed a retrospective study of 123 patients were, of whom 42% had confirmed PCP, 18% had possible PCP, and 40% were negative for PCP. . Immunosuppressive conditions consisted mostly of diffuse connective tissue disease (50%) and primary nephropathy (20%).
An induced sputum was performed for all patients; however, if this was not possible or suboptimal, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was also done. Patients who were intubated at the time of clinical suspicion for PCP had both induced sputum and BAL performed. Gomori–Grocott methenamine silver nitrate staining (GMS) was performed on all samples obtained. A qualitative P. jirovecii polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was performed using either specimen, as requested by the treating physicians. Fungal DNA was extracted using a QIAamp MinElute Virus Spin Kit.
The team found that independent predictors of PCP were a CD3+ cell count of less than 625 × 106/L, serum albumin less than 28 g/L, and partial pressure of oxygen in arterial blood/ fractional inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratio of less than 210. Furthermore, 90% of patients with PCP had a CD3+ cell count less than 750 × 106/L. Independent predictors of mortality were a CD8+ cell count less than 160 × 106/L and a PaO2/FiO2 ratio of less than 160. All groups displayed absolute lymphocytopenia on admission, but more severe cytopenias were present in patients with confirmed PCP. Those with confirmed PCP had a significantly lower total lymphocyte count and lower lymphocyte subtype counts (CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+) than PCP-negative patients.
The authors concluded that only patients with inflammatory and autoimmune conditions receiving immunosuppressive therapy, a CD3+ cell count below 625 × 106/L, severe hypoxemia, and a low serum albumin concentration were found to be independent predictors of PCP. These results also suggest that anti-PCP prophylaxis should be considered in this population when the CD3+ cell count is below 750 × 106/L, although this would require validation in prospective studies. The study was published in the April 2017 edition of the International Journal of Infectious Diseases.









 (3) (1).png)




