Handheld Mass Spectrometer Identifies Cancer Tissue in Seconds
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 19 Sep 2017
A team of scientists and engineers has invented a powerful device that rapidly identifies living cancerous tissue, giving surgeons precise diagnostic information about what tissue to cut or preserve.Posted on 19 Sep 2017
“If you talk to cancer patients after surgery, one of the first things many will say is ‘I hope the surgeon got all the cancer out’,” said Livia Schiavinato Eberlin, assistant professor at University of Texas at Austin (Austin, TX, USA) who designed the study and led the team, “our technology could vastly improve the odds that surgeons really do remove every last trace of cancer during surgery.”
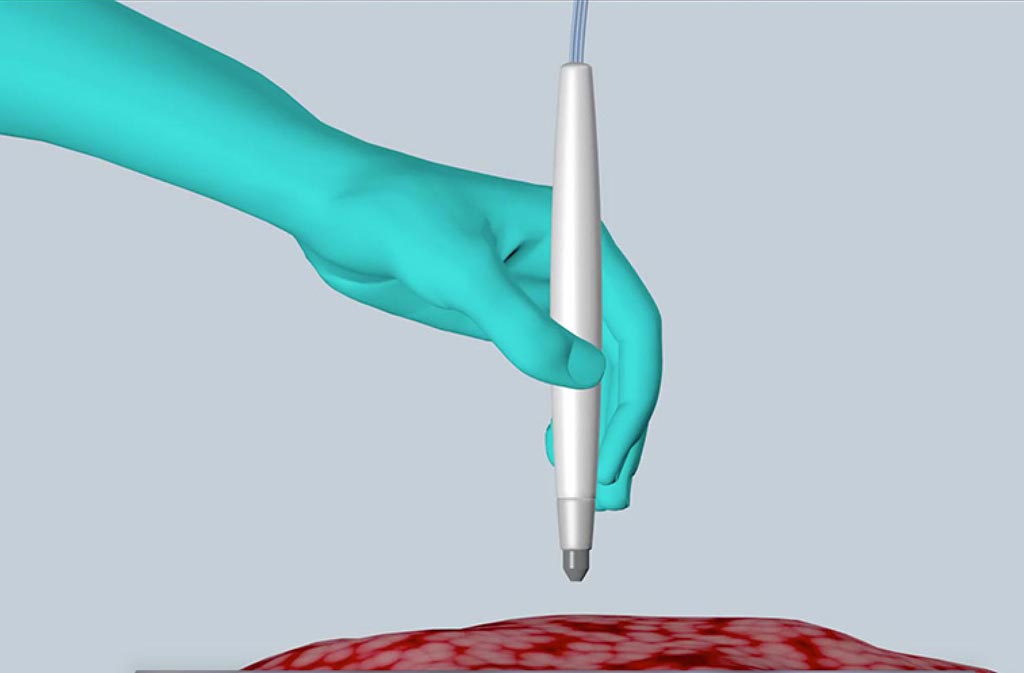
Image: The MasSpec Pen rapidly and accurately detects live cancer during surgery, helping improve treatment and reduce the chances of cancer recurrence (Photo courtesy of the University of Texas at Austin).
The current method, Frozen Section Analysis, for diagnosis and determining the boundary between cancer and normal tissue during surgery is slow and sometimes inaccurate. Each sample can take 30 minutes or more to prepare and interpret by a pathologist, increasing risk to the patient of infection and negative effects of anesthesia. For some types of cancers frozen section interpretation can be difficult, often yielding unreliable results.
The new MasSpec Pen took about 10 seconds to provide a diagnosis and was over 96% accurate in tests on tissues removed from 253 human cancer patients. It also detected cancer in marginal regions between normal and cancer tissues that presented mixed cellular composition.
This technology also offers the patient a safer surgery. “It allows us to be much more precise in what tissue we remove and what we leave behind,” said project collaborator James Suliburk, of Baylor College of Medicine. Although maximizing cancer removal is critical, removing too much healthy tissue can also have profound negative consequences: For example, breast cancer patients could experience higher risk of painful side effects and nerve damage, in addition to aesthetic impacts. Thyroid cancer patients could lose speech ability or the ability to regulate the body’s calcium levels in ways important for muscle and nerve function.
Living cells produce metabolites and each type of cancer produces a unique set of metabolites and other biomarkers. “Because the metabolites in cancer and normal cells are so different, we extract and analyze them with the MasSpec Pen to obtain a molecular fingerprint of the tissue. What is incredible is that through this simple and gentle chemical process, the MasSpec Pen rapidly provides diagnostic molecular information without causing tissue damage,” said Prof. Eberlin.
The molecular fingerprint obtained by the MasSpec Pen from an uncharacterized tissue sample is instantaneously evaluated by a “statistical classifier” software trained on a database of molecular fingerprints that Prof. Eberlin and her colleagues gathered from the 253 human tissue samples. The samples included both normal and cancerous tissues of the breast, lung, thyroid, and ovary.
The pen releases a drop of water onto the tissue, and small molecules migrate into the water. The water sample is driven into a mass spectrometer, which detects thousands of molecules as a molecular fingerprint. The disposable device requires simply holding the pen against the patient’s tissue, triggering the automated analysis using a foot pedal, and waiting a few seconds for a result.
In tests performed on human samples, the device was more than 96% accurate for cancer diagnosis. It also diagnosed cancer in live, tumor-bearing mice during surgery without causing observable tissue harm or stress to the animals.
So the process would be low-impact for patients and biocompatible. “When designing the MasSpec Pen, we made sure the tissue remains intact by coming into contact only with water and the plastic tip of the MasSpec Pen during the procedure,” said Prof. Zhang.
The study, by Zhang J et al, was published September 6, 2017, in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
Related Links:
University of Texas at Austin











 (3) (1).png)


