Cell-Specific Bioorthogonal Tagging of Glycoproteins Developed
Posted on 31 Oct 2022
Altered glycoprotein expression is an undisputed corollary of cancer development. Understanding these alterations is paramount but hampered by limitations underlying cellular model systems. For instance, the intricate interactions between tumor and host cannot be adequately recapitulated in monoculture of tumor-derived cell lines.
Cancer is a multifactorial disease consisting of an interplay between host and tumor. Posttranslational modifications (PTMs) heavily impact the plasticity of the proteome. Glycosylation is the most complex and most abundant PTM, but challenging to probe due to the non-templated nature of glycan biosynthesis.
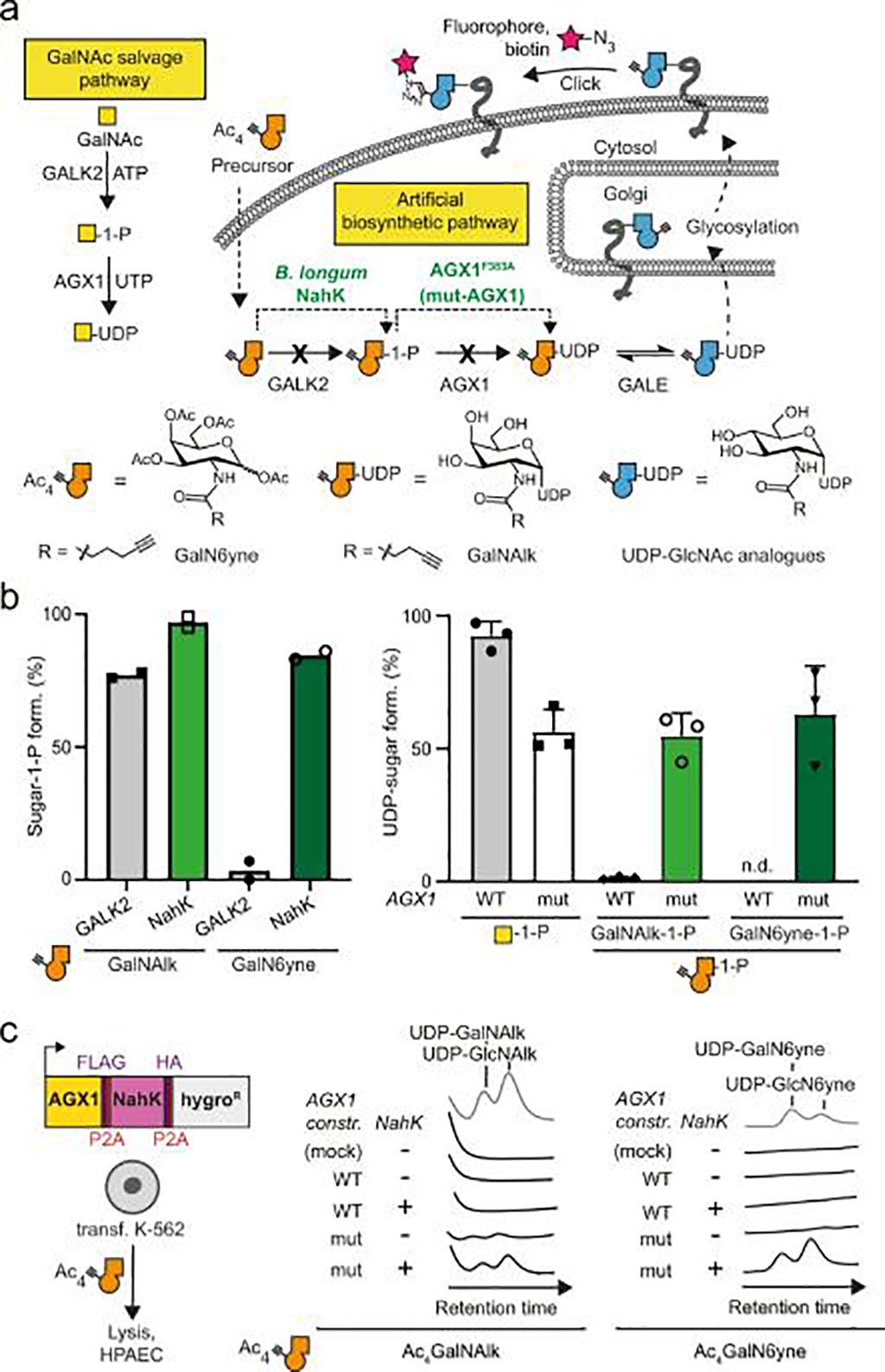
Chemists and Biochemists at the Imperial College London (London, UK) have developed a new method to study the proteins released by cells, which could lead to the development of new tools to track diseases including cancer. Their method identifies proteins released by a specific type of cell, even if the cells are in a complex environment with many different cell types. The method is called Bio-Orthogonal Cell line-specific Tagging of Glycoproteins (BOCTAG).
The method uses bioorthogonal chemistry or click chemistry. The chemical tag is selected so that it "clicks" with another molecule that helps the scientists isolate the desired proteins or add a fluorescent tag to them. The investigators showed that BOCTAG worked in cell cultures with multiple cell lines and in mice, where they successfully tagged proteins from specific cancer cells. This method could also be used in fields such as immunology, infectious diseases, and to better understand disease biology, particularly how tumor cells change as a result of complex interactions in the body.
Cells are equipped by transfection with an artificial biosynthetic pathway that transforms bioorthogonally tagged sugars into the corresponding nucleotide-sugars. Only transfected cells incorporate bioorthogonal tags into glycoproteins in the presence of non-transfected cells. The team employed BOCTAG as an imaging technique and to annotate cell-specific glycosylation sites in mass spectrometry-glycoproteomics using Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS) equipped with a ACQUITY UPLC BEH Glycan (Waters Corporation, Milford, MA, USA). They demonstrated application in co-culture and mouse models, allowing for profiling of the glycoproteome as an important modulator of cellular function. The study was published on October 25 2022 in the journal Nature Communications.
Related Links:
Imperial College London
Waters Corporation














