Endothelial Function Biomarker Improves Sepsis Patients Risk Stratification
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 18 Mar 2020
Sepsis is a potentially life-threatening condition caused by the body's response to an infection. The body normally releases chemicals into the bloodstream to fight an infection. Sepsis occurs when the body's response to these chemicals is out of balance, triggering changes that can damage multiple organ systems.Posted on 18 Mar 2020
Biomarkers to diagnose sepsis may allow early intervention which, although primarily supportive, can reduce the risk of death. Lactate, a parameter that identifies reduced blood oxygenation of tissue, is routinely used as a reference in the diagnosis of septic shock. However, lactate is rather unspecific to sepsis and insensitive.
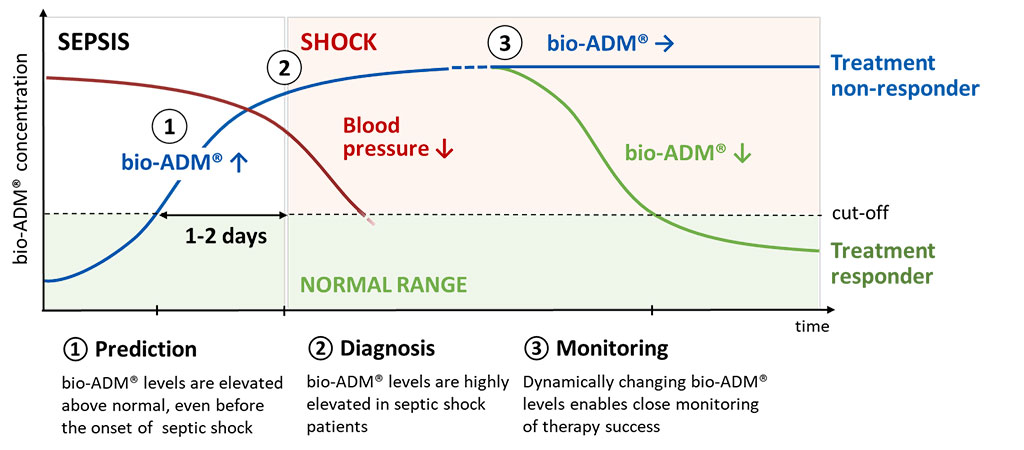
Image: Endothelial function biomarker adrenomedullin as assayed by bio-ADM improves sepsis patients risk stratification (Photo courtesy of sphingotec).
Critical care physicians at the Hôpital Lariboisière (Paris, France) are part of the AdrenOSS-1 study which is a prospective observational study conducted in 24 centers within five European countries and included 583 septic patients from June 2015 to May 2016. The primary endpoint was 28-day mortality.
The team evaluated the relationship between the association of initial evolution of lactate plasma levels and endothelial function biomarker bioactive Adrenomedullin (bio-ADM) level at 24 hours and outcome in patients for whom both markers were available at admission and one day later. Adrenomedullin is a vasodilatory hormone that regulates blood pressure and plays an essential role in the development of acute circulatory failure. The scientists used bio-ADM levels below or above 70 pg/mL which were considered respectively as low and high. The bio-ADM was measured by an assay from sphingotec GmbH (Hennigsdorf Germany).
The AdrenOSS-1 study investigators showed that even though normalizing lactate levels indicate a significantly decreased risk of mortality, an additional measurement of bio-ADM blood levels can help identify those patients that are still at risk of fatal outcomes despite their lower lactate levels. Among septic patients with decreasing lactate, high bio-ADM levels identified patients who had a 4-time higher mortality risk than patients with low bio-ADM levels. According to the authors of the study, measurement of bio-ADM, as well as lactate, may help refine risk stratification and thus guide resuscitation during sepsis.
Andreas Bergmann, PhD, CEO and founder of sphingotec, said, “Our biomarker bio-ADM can reliably support acute care physicians in identifying high-risk sepsis patients. We are set to launch the fully automated CE-IVD-marked point-of-care bio-ADM assay on our widely established Nexus IB10 immunoassay instrument by mid-2020. We are convinced that this rapid test for bio-ADM will support earlier treatment decisions and thereby will assist clinical decisions that may improve the outcomes of patients at ICUs and emergency departments.” The study was published on February 28, 2020 in the journal Critical Care.
Related Links:
Hôpital Lariboisière
Sphingotec













