Glycemic Variability Predicts Major Adverse Cardiac Event
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 19 Mar 2019
Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) are a composite endpoint frequently used in cardiovascular studies, comparable to the composite endpoint all-cause mortality. Despite widespread use of the term in clinical trials, the definitions of MACE can differ, which makes comparison of similar studies difficult.Posted on 19 Mar 2019
Acute glucose fluctuations are associated with hypoglycemia and are emerging risk factors for cardiovascular outcomes. However, the relationship between glycemic variability (GV) and the occurrence of midterm MACE in patients with diabetes remains unclear. A glycemic variability cutoff value could be the strongest independent predictive factor for midterm MACE in patients with diabetes and acute coronary syndrome.
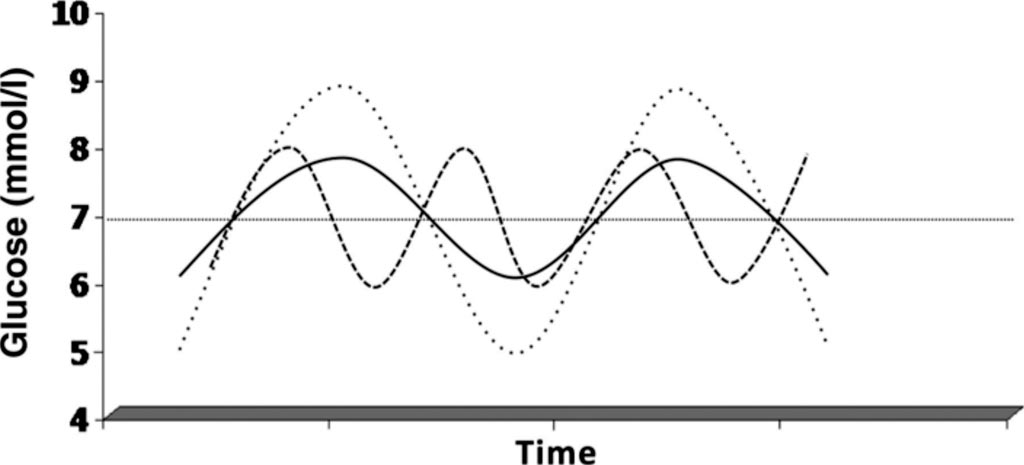
Image: A visualization of glucose variability. Solid line: a given excursion. Dashed line: higher glucose variability due to a higher frequency of oscillation. Dotted line: higher glucose variability due to larger amplitude. Note that the mean and area under the curve are identical in the three situations (Photo courtesy of J. Hans DeVries MD, PhD).
Medical scientists at the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Bordeaux (Bordeaux, France) and their colleagues investigated the relationship between glycemic variability and the occurrence of midterm MACE. The team assessed glycemic variability in 327 consecutive patients (mean age, 69 years) hospitalized with diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. Each patient was evaluated for glycemic variability at enrollment and was monitored during follow-up for such major cardiovascular events as new-onset myocardial infarction, acute heart failure, and cardiac death.
The investigators reported that of the study population, 89 (27.2%) people experienced a major cardiovascular event during a mean follow-up of 16.9 months; 24 patients died of cardiac causes, 35 had new-onset myocardial infarction, and 30 were hospitalized because of acute heart failure. Using multivariable logistic regression analysis, they found multiple independent predictive factors of midterm major cardiovascular events, including a glycemic variability value greater than 2.7 mmol/L (odds ratio [OR] = 2.21); a synergy between Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI) with Taxus and Cardiac Surgery score greater than 34 (OR = 1.88), and reduced ventricular ejection fraction of less than 40%. A Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events risk score greater than 140 was not predictive (OR = 1.07).
The authors concluded that a GV cutoff value of greater than 2.70 mmol/L was the strongest independent predictive factor for midterm MACE in patients with diabetes and acute coronary syndrome. The study was published in the February 2019 issue of the journal Diabetes Care.
Related Links:
Centre Hospitalier Universitaire de Bordeaux














