Parent Age May Help Predict AD Biomarker Levels
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 14 Mar 2018
Alzheimer disease (AD) develops during several decades and presymptomatic individuals might be the best candidates for clinical trials, but their identification is challenging because they have no symptoms.Posted on 14 Mar 2018
Asymptomatic people with a family history of sporadic AD were more likely to show abnormal cerebrospinal fluid and brain amyloid- biomarkers as they neared their parent’s onset age, indicating that proximity to parental symptom onset may help predict amyloid- biomarker changes.
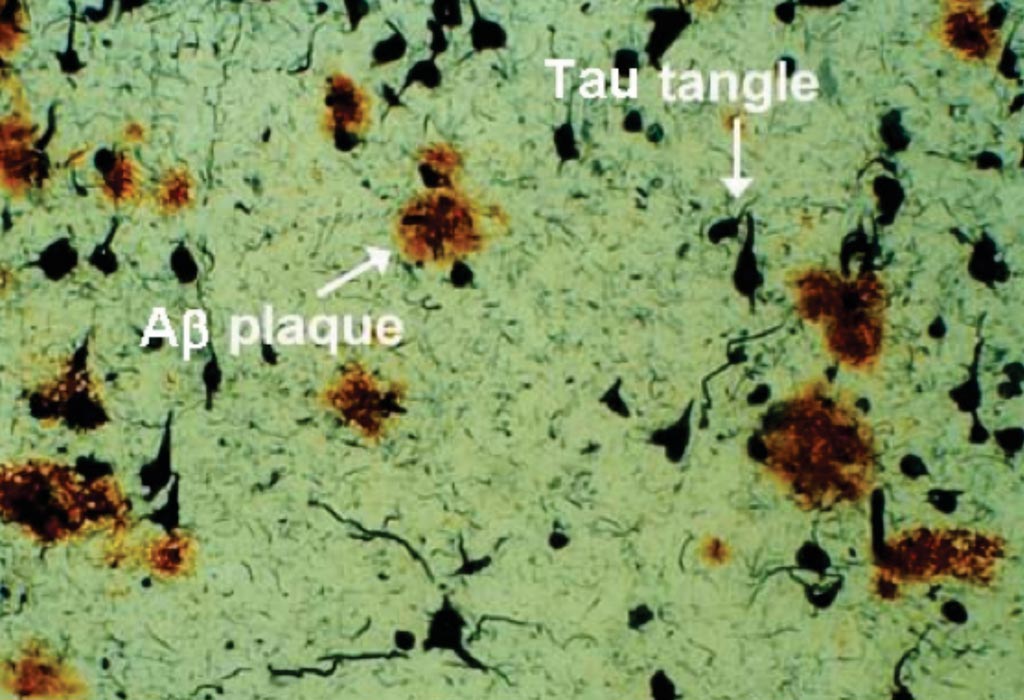
Image: Postmortem tissue sample from an Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patient brain reveals AD pathology including amyloid-beta plaques and Tau tangles (Photo courtesy of Dr. Dale Bredesen).
A team of scientists led by those at McGill University (Montreal, QC, Canada) analyzed amyloid-1-42 (Aβ1-42) in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) specimens from 101 cognitively unimpaired individuals enrolled in the Presymptomatic Evaluation of Novel or Experimental Treatments for Alzheimer Disease (PREVENT-AD) cohort from September 1, 2011, through November 30, 2016. Along with a subset of the 101 PREVENT-AD participants, analysis included 128 Adult Children Study (ACS) participants (112 of whom underwent CSF measurement and 107 of whom underwent Pittsburgh compound B carbon 11–labeled positron emission tomography (PIB-PET) and 135 Wisconsin Registry for Alzheimer Prevention (WRAP) participants (85 of whom underwent CSF measurement and all of whom underwent PIB-PET).
The scientists found that PREVENT-AD participants nearing their parent’s Alzheimer’s disease onset age had lower CSF amyloid-1-42 levels; this relationship was stronger in APOE4 carriers and women. Among ACS participants, the team observed the same association using PIB-PET data, and using CSF and PIB-PET data also replicated the female sex interaction. Although the findings were not replicated using cross-sectional data among WRAP participants, the link between parent’s Alzheimer’s disease onset age and CSF amyloid- levels and the APOE interaction were replicated using PIB-PET longitudinal data.
Sylvia Villeneuve, PhD, the lead author of the study, said, “The best time window to prevent Alzheimer’s disease is likely when individuals are still asymptomatic, before extensive neuronal degeneration has occurred. Identifying asymptomatic individuals is challenging and expensive, posing significant difficulties for the current generation of clinical trials. In autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease, symptom onset is determinable across generations.”
The authors concluded that their results suggest that proximity to parental symptom onset may help estimate Aβ biomarker changes in women or APOE4 carrier asymptomatic individuals with a parental history of sporadic AD. The study was published on February 26, 2018, in the journal JAMA Neurology.
Related Links:
McGill University














