Peptide Serum Markers Predict Type 1 Diabetes
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 01 Dec 2016
Certain proteins in the blood of children can predict incipient type 1 diabetes, even before the first symptoms appear. Children who have a first-degree relative with type 1 diabetes and who consequently have an increased risk of developing the disease due to the familial predisposition.Posted on 01 Dec 2016
This autoimmune process does not develop from one day to the next. Often the young patients go through longer asymptomatic preliminary stages that see the formation of the first antibodies against the child's own insulin-producing cells in the pancreas; these are the so-called autoantibodies. Biomarkers that indicate whether and when this is the case and how quickly the clinical symptoms will appear could significantly improve the treatment of patients at-risk.
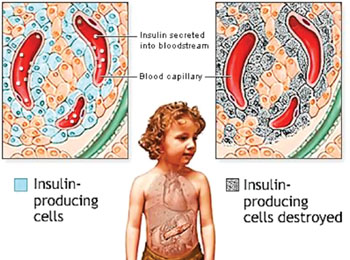
Image: A diagram of Type1 diabetes as an autoimmune disease (Photo courtesy of the US National Institutes of Health).
Scientists at the Helmholtz Zentrum München (Munich, Germany) and their colleagues analyzed blood samples from 30 children with autoantibodies who had developed type 1 diabetes either very rapidly or with a very long delay. The team compared the data with data on children who displayed neither autoantibodies nor diabetes symptoms. In a second step with samples from another 140 children, they confirmed the protein composition differences that they found in this approach.
A double cross-validation approach was applied to first prioritize peptides from a shotgun proteomic approach in 45 islet autoantibody-positive and -negative children. Targeted proteomics for 82 discriminating peptides were then applied to samples from another 140 children from these cohorts. A total of 41 peptides (26 proteins) enriched for the functional category lipid metabolism were significantly different between islet autoantibody-positive and autoantibody-negative children. Two peptides from apolipoprotein M and apolipoprotein C-IV were sufficient to discriminate autoantibody-positive from autoantibody-negative children. Hepatocyte growth factor activator, complement factor H, ceruloplasmin and age predicted progression time to type 1 diabetes with a significant improvement compared with age alone.
Anette‐Gabriele Ziegler, MD, PhD, a professor and a senior author of the study, said, “The progression of type 1 diabetes into a clinical disease takes place over a period of time that varies from individual to individual and that at this time is insufficiently predictable. The biomarkers that we have identified allow a more precise classification of this presymptomatic stage and they are relatively simple to acquire from blood samples.” The study was published on November 4, 2016, in the journal Diabetologia.
Related Links:
Helmholtz Zentrum München








 Analyzer.jpg)





