High Cholesterol Linked to Risk of Tendinopathy
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 03 Nov 2015
People with genetically determined very high cholesterol levels, as in familial hypercholesterolaemia, seem to be at greater risk of tendon pain, but it is not clear if those with lower, but still high levels might also be vulnerable to tendon injuries. Posted on 03 Nov 2015
Tendons are the tough fibers connecting muscles and bones in the body. Mechanical stress as a result of obesity or excess body fat distribution, and overuse during the course of exercise or work, are thought to be among the leading causes of tendon injuries or tendinopathy.
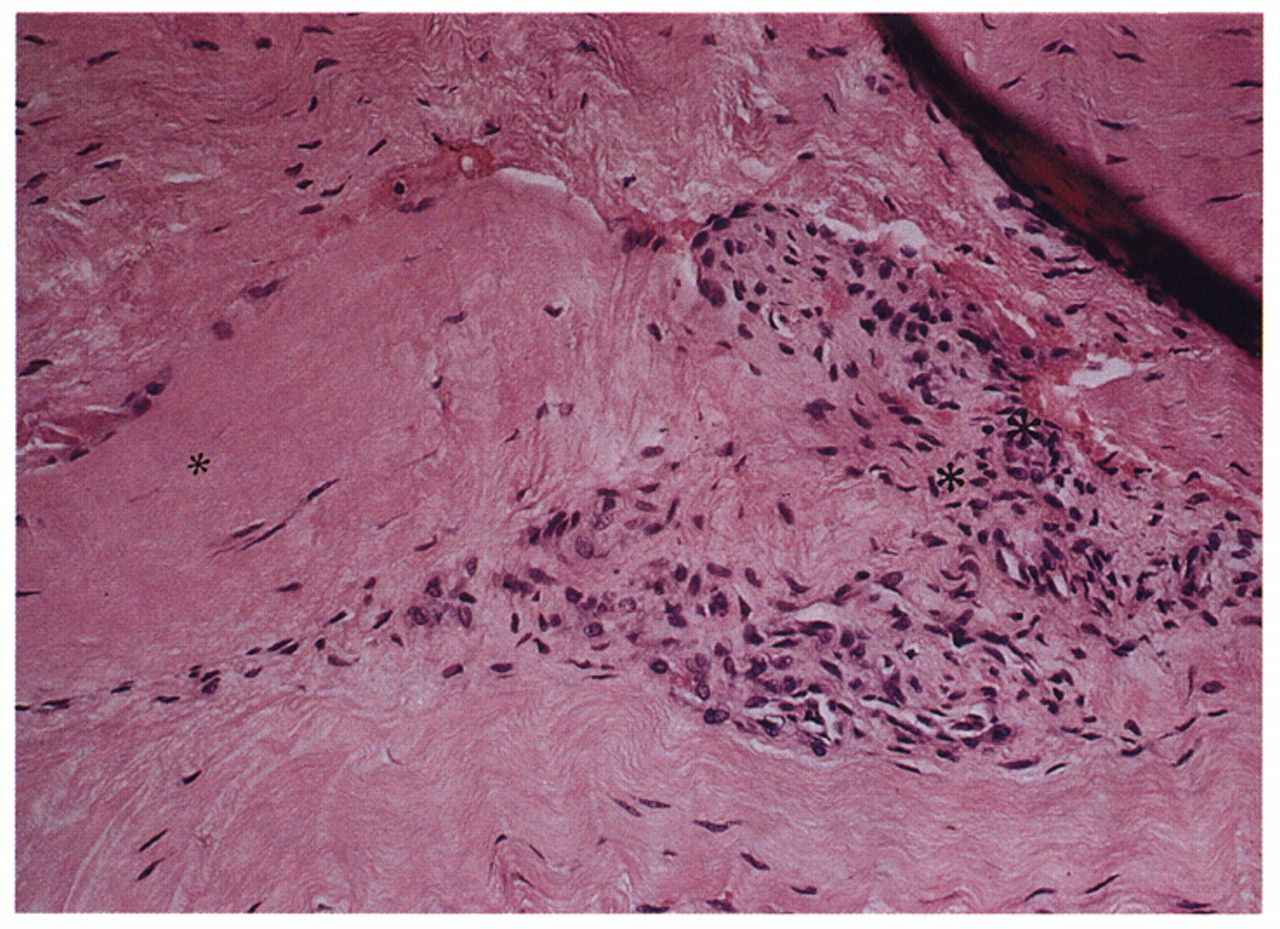
Image: Histologic appearance of tendinosis tissue shows a characteristic pattern of fibroblasts and vascular, atypical, granulation-like tissue (Photo courtesy of Dr. Barry S. Kraushaar, MD).
Scientists at the Monash University (Melbourne, Australia) conducted a systematic review of six medical databases, looking for studies investigating links between blood fats and tendon abnormalities or pain. They found with 1,607 relevant articles, of which 17, involving 2,612 participants, and published between 1973 and 2014, were suitable for inclusion in the analysis. A meta-analysis was conducted for each of the four lipid measurements: total cholesterol (TC), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and triglycerides (TG)), and their individual association with tendon structure or tendon pain.
Total cholesterol (TC) was significantly higher among individuals with tendon pain or rupture, with a mean difference (MD) of 0.66 mmol/L; HDL-C was significantly lower among individuals with tendon pain or rupture with MD equal to 0.19 mmol/L; and LDL-C was significantly higher among individuals with tendon pain or rupture, the MD was 1.00 mmol/L; and TG was significantly higher among individuals with tendon pain or rupture, the MD was 0.33 mmol/L. Furthermore, people with an unfavorable lipid profile were much more likely to have tendon injuries and higher levels of pain associated with musculoskeletal problems in their arms.
The authors concluded that the results of the review indicate that a relationship exists between an individual’s lipid profile and tendon health. However, further longitudinal studies are required to determine whether a cause and effect relationship exists between tendon structure and lipid levels. This could lead to advancement in the understanding of the pathoetiology and thus treatment of tendinopathy. The study was published on October 15, 2015, in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
Related Links:
Monash University














