Near Real-Time Osteoporosis and Bone Cancer Test Developed
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 31 Aug 2015
A new test which measures changes in calcium isotope ratios offers the possibility of near real time monitoring of bone diseases, such as osteoporosis and multiple myeloma.Posted on 31 Aug 2015
Bones are largely built of calcium, and the turnover of calcium can indicate the development of bone diseases such as osteoporosis and the cancer multiple myeloma and using techniques developed by geochemists it was found possible to apply them to a new, rapid test of bone health.
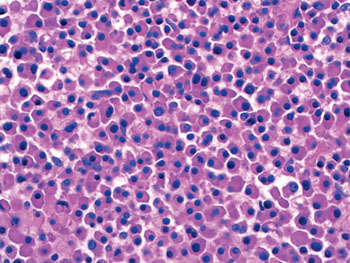
Image: Photomicrograph demonstrating typical multiple myeloma histology, with monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells (Photo courtesy of Ohio State University College of Medicine).
Scientists at Arizona State University (Tempe, AZ, USA) worked with the US National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA, Washington DC, USA) and measured calcium isotope ratios in urine from 30 shuttle astronauts, before, during, and after the flights. This allowed them to confirm that the test worked at high sensitivity. They also looked at a group of 71 patients who either had multiple myeloma (bone cancer), or were at risk of multiple myeloma.
The methodology used mass spectrometry and can discern the relative ratios of the calcium isotopes 42Ca and 44Ca in bone. The researchers found that lighter calcium isotopes, such as 42Ca, are absorbed from the blood into the bone during bone formation. Conversely, these light isotopes tend to be released into the bloodstream when bones break down. By measuring the ratios of the two isotopes in blood or urine scientists can calculate the rate of change of bone mass.
Ariel Anbar, PhD, the lead scientists of the study said, “What we saw with cancer patients was interesting. Those patients who tended to lose the lighter 42Ca isotope seemed to be the ones where the cancer was the most active. This means that the tests could theoretically feed into decisions on whether or not to treat a patient, for example if a cancer was dormant or growing very slowly, and to assess the effectiveness of treatments. The advantage for this methodology is that the patient doesn't have to come to the machine; the measurements can be done with a blood or urine test.”
Related Links:
Arizona State University
US National Aeronautics and Space Administration














