Less Toxic Drugs May Replace Current Chemotherapeutic Agents
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 04 Apr 2018
A team of South African cancer researchers has suggested replacing the current frontline platinum-based chemotherapeutic drugs with first generation silver(I) phosphines, which have vast structural diversity and promising anticancer activity.Posted on 04 Apr 2018
Increased incidences of cancer, side-effects to chemotherapeutic agents and redevelopment of tumors due to resistance has prompted the search for alternative compounds showing anticancer activity.
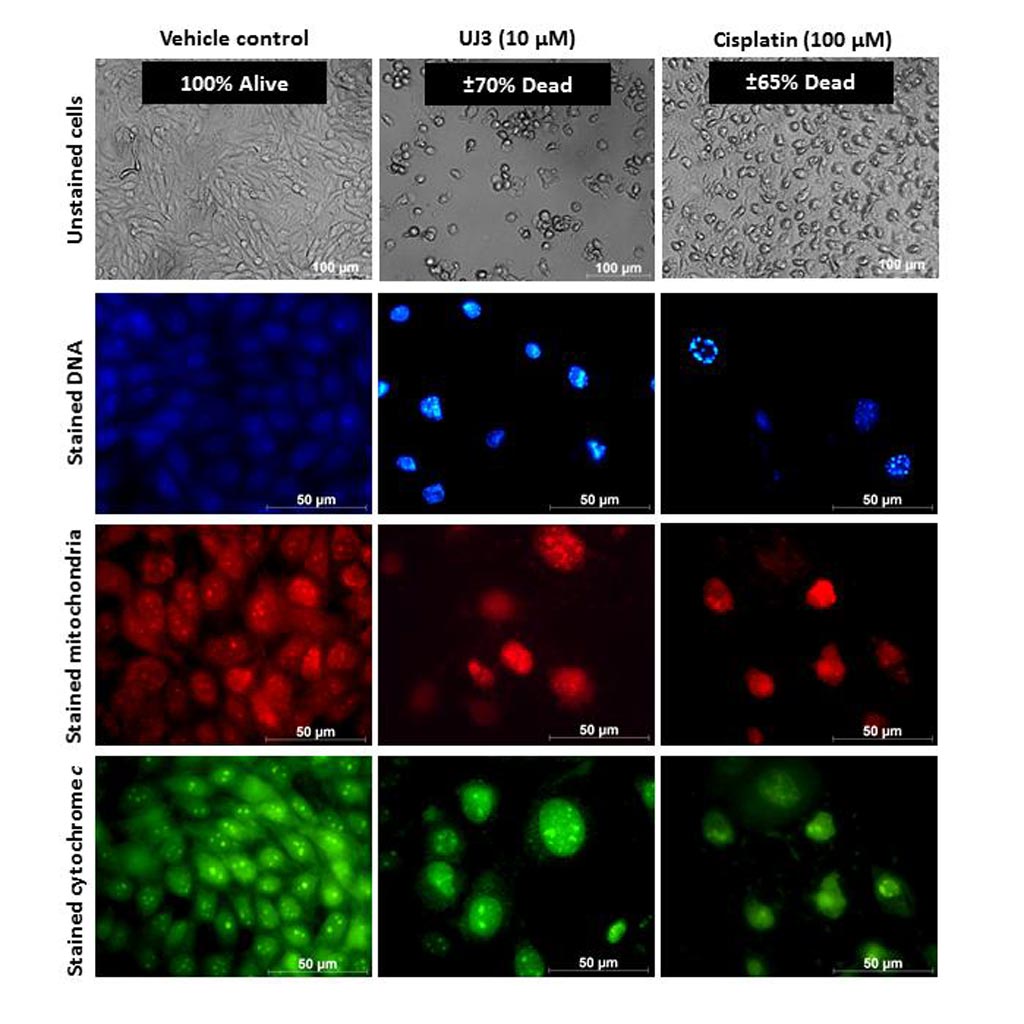
Image: A family of economical silver-based complexes shows very promising results against a number of human cancers in laboratory tests, with very low toxicity in rat studies and minimal effects on healthy cells. One of these complexes, UJ3, is as effective as the industry-standard drug Cisplatin in killing cancer cells in laboratory tests done on human esophageal cancer, breast cancer, and melanoma. This matrix of light microscope images shows a comparison of human esophageal cancer cells treated with UJ3 and Cisplatin (Photo courtesy of Dr. Zelinda Engelbrecht, University of Johannesburg).
A fruit of this search has been the discovery by investigators at the University of Johannesburg (South Africa) of a new family of promising silver-based anti-cancer drugs. The most promising silver thiocyanate phosphine complex among these, called UJ3, was tested in rats and in human cancer cell cultures.
Results of the study published in the April 2018 issue of the journal BioMetals revealed the effective induction of cell death by a silver(I) thiocyanate 4-methoxyphenyl phosphine complex (UJ3) in a malignant esophageal cell line. Apoptotic cell death was confirmed in treated cells. Moreover, mitochondrial targeting via the intrinsic cell death pathway was evident due to low levels of ATP, altered ROS (reactive oxygen species) activity, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, cytochrome c release, and caspase-9 cleavage.
The complex silver(I) phosphine complex displayed low cytotoxicity towards two human non-malignant, skin and kidney, cell lines.
"In rat studies, we see that up to three grams of UJ3 can be tolerated per one kilogram of bodyweight. This makes UJ3 and other silver phosphine complexes we have tested about as toxic as vitamin C," said senior author Dr. Reinout Meijboom, professor of chemistry at the University of Johannesburg. "These complexes can be synthesized with standard laboratory equipment, which shows good potential for large scale manufacture. The family of silver thiocyanate phosphine compounds is very large. We were very fortunate to test UJ3, which has an unusually "flat" chemical structure, early on in our exploration of this chemical family for cancer treatment."
Related Links:
University of Johannesburg