Levels of SIRT6 Linked to Neurodegenerative Disease
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 30 May 2017
Low levels of the protein SIRT6 (Sirtuin-6) have been linked to aging-like changes in cells including the hyperphosphorylation of Tau, a critical marker in several neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's.Posted on 30 May 2017
SIRT6 is a chromatin-associated protein that is required for normal base excision repair of DNA damage in mammalian cells. Deficiency of SIRT6 in mice leads to abnormalities that overlap with aging-associated degenerative processes. SIRT6 also promotes the repair of DNA double-strand breaks by the process of non-homologous end joining.
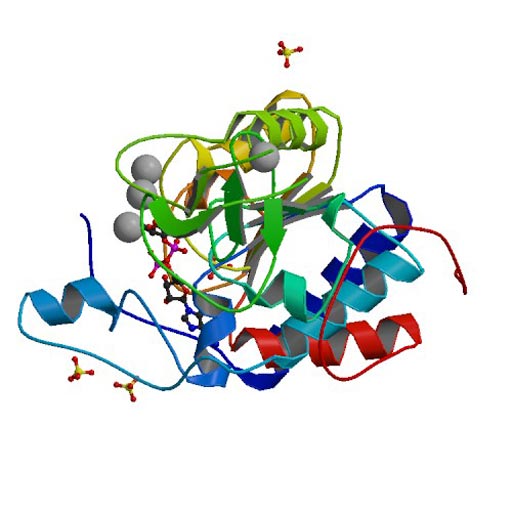
Image: The structure of the human SIRT6 protein (Photo courtesy of the Protein Data Bank).
Investigators at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev worked with a line of mice that had been genetically engineered to lack the gene for SIRT6 specifically in brain tissue. They reported in the March 28, 2017, issue of the journal Cell Reports that while knockout mice completely lacking SIRT6 exhibited an accelerated aging phenotype and died prematurely, brain-specific SIRT6-deficient mice survived but presented behavioral defects with major learning impairments by four months of age. The brains of these mice showed increased signs of DNA damage, cell death, and hyperphosphorylated Tau.
At the molecular level SIRT6 was found to regulate Tau protein stability and phosphorylation through increased activation of the kinase enzyme glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha/beta (GSK3alpha/beta).
The investigators also found that SIRT6 was almost completely absent in Alzheimer's disease patients, a finding that suggested to them that SIRT6 was critical for maintaining genomic stability in the brain and that its loss led to toxic Tau stability and phosphorylation.
Senior author Dr. Deborah Toiber, a molecular biologist at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, said, "If a decrease in SIRT6 and lack of DNA repair is the beginning of the chain that ends in neurodegenerative diseases in seniors, then we should be focusing our research on how to maintain production of SIRT6 and avoid the DNA damage that leads to these diseases."