Blood-based Liquid Biopsy Detects Lymph Node Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer Patients
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 04 May 2021 |
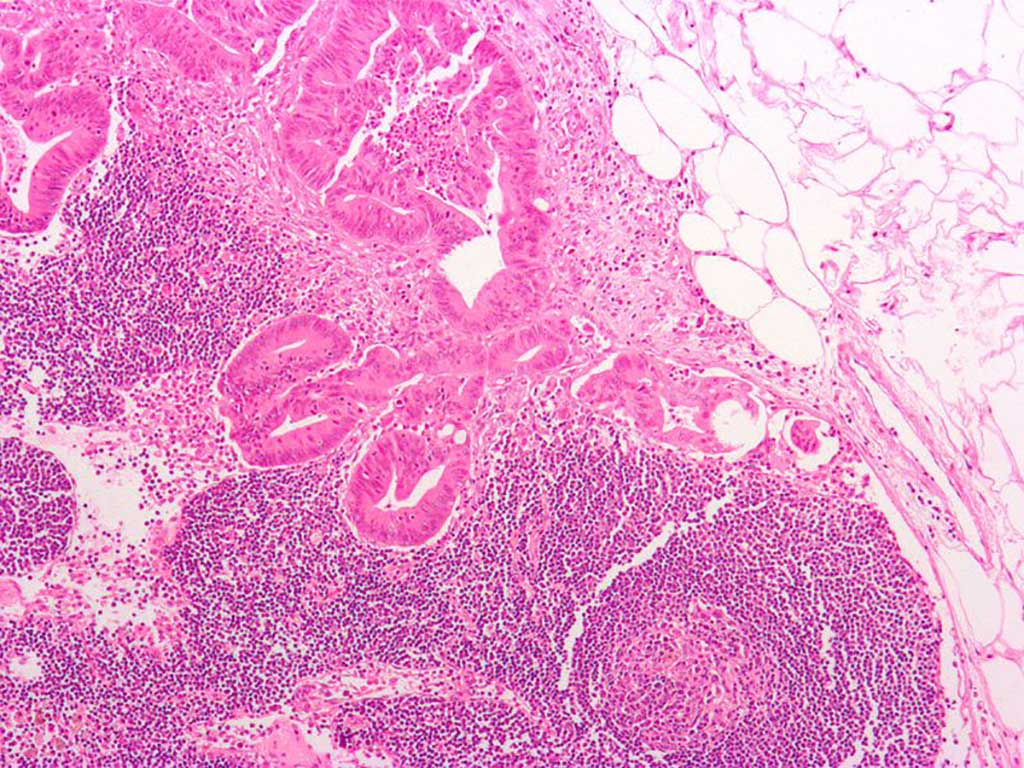
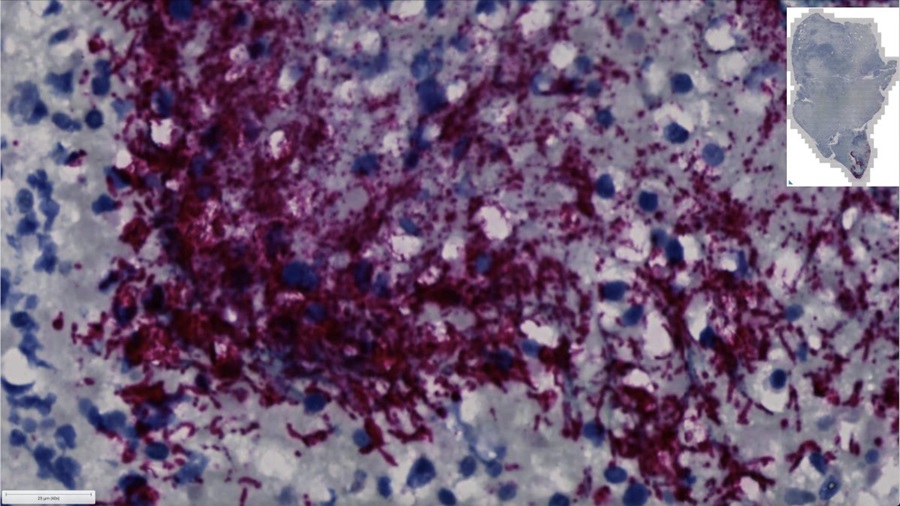
Image: Micrograph of a colorectal adenocarcinoma metastasis to a lymph node. The cancer (forming glands) is seen at the center-top. Adipose tissue is present on the upper right (Photo courtesy of Wikimedia Commons)
A recent paper described a novel, noninvasive liquid biopsy test for detection of lymph node metastasis in individuals with high-risk T1 colorectal cancer.
Local cancer in many parts of the body can cause lymph nodes to enlarge because of tumor cells that have metastasized into the node. Lymph node involvement is often a key factor in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. As part of the investigations or workup for cancer, lymph nodes may be imaged or even surgically removed. Whether lymph nodes are affected will affect the staging of the cancer and overall treatment and prognosis.
Investigators at City of Hope (Duarte, CA, USA) had previously used surgically resected tissue specimens and endoscopic biopsies taken during colonoscopy to establish a panel of miRNAs and mRNAs for the identification of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in invasive submucosal colorectal cancers (T1 CRC). In the current study, they translated these tissue-based biomarkers into a noninvasive blood-based liquid biopsy assay.
The investigators analyzed 330 specimens from patients with high-risk T1 CRC, which included 188 serum samples from two clinical cohorts and matched FFPE (formalin-fixed-paraffin-embedded) samples. They performed RT-qPCR followed by logistic regression analysis to develop an integrated transcriptomic panel and establish a risk-stratification model, combined with clinical risk factors.
The liquid biopsy test was found to accurately identify lymph node metastasis with high sensitivity (83.3%) and specificity (76.2%). These results enabled the investigators to identify an optimized transcriptomic panel of four miRNAs (miR-181b, miR-193b, miR-195, miR-411) and five mRNAs (AMT, FOXA1, PIGR, MMP1, MMP9), which robustly identified patients with LNM. Application of this diagnostic model limited potential over-treatment to only 18% of all patients, which was dramatically superior to currently used models based on pathological features (92%).
"Since radical surgery dramatically reduces quality of life for patients, improving the success rate of identification of high-risk individuals with lymph node metastasis remains the challenge in T1 colorectal cancer diagnosis," said senior author Dr. Ajay Goel, chair of the department of molecular diagnostics and experimental therapeutics at City of Hope. "In the future, we hope to improve our confidence in identifying which individuals truly have lymph node metastasis via this novel biomarker-based liquid biopsy test for T1 colorectal cancer, in combination with clinical and pathological criteria. Obtaining results with more than 80% accuracy (sensitivity) in finding lymph node metastasis in the blood was a completely unexpected finding and is a complete game changer."
The blood-based liquid biopsy for detection of lymph node metastasis was described in the April 2, 2021, online edition of the journal Gastroenterology.
Related Links:
City of Hope
Local cancer in many parts of the body can cause lymph nodes to enlarge because of tumor cells that have metastasized into the node. Lymph node involvement is often a key factor in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer. As part of the investigations or workup for cancer, lymph nodes may be imaged or even surgically removed. Whether lymph nodes are affected will affect the staging of the cancer and overall treatment and prognosis.
Investigators at City of Hope (Duarte, CA, USA) had previously used surgically resected tissue specimens and endoscopic biopsies taken during colonoscopy to establish a panel of miRNAs and mRNAs for the identification of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in invasive submucosal colorectal cancers (T1 CRC). In the current study, they translated these tissue-based biomarkers into a noninvasive blood-based liquid biopsy assay.
The investigators analyzed 330 specimens from patients with high-risk T1 CRC, which included 188 serum samples from two clinical cohorts and matched FFPE (formalin-fixed-paraffin-embedded) samples. They performed RT-qPCR followed by logistic regression analysis to develop an integrated transcriptomic panel and establish a risk-stratification model, combined with clinical risk factors.
The liquid biopsy test was found to accurately identify lymph node metastasis with high sensitivity (83.3%) and specificity (76.2%). These results enabled the investigators to identify an optimized transcriptomic panel of four miRNAs (miR-181b, miR-193b, miR-195, miR-411) and five mRNAs (AMT, FOXA1, PIGR, MMP1, MMP9), which robustly identified patients with LNM. Application of this diagnostic model limited potential over-treatment to only 18% of all patients, which was dramatically superior to currently used models based on pathological features (92%).
"Since radical surgery dramatically reduces quality of life for patients, improving the success rate of identification of high-risk individuals with lymph node metastasis remains the challenge in T1 colorectal cancer diagnosis," said senior author Dr. Ajay Goel, chair of the department of molecular diagnostics and experimental therapeutics at City of Hope. "In the future, we hope to improve our confidence in identifying which individuals truly have lymph node metastasis via this novel biomarker-based liquid biopsy test for T1 colorectal cancer, in combination with clinical and pathological criteria. Obtaining results with more than 80% accuracy (sensitivity) in finding lymph node metastasis in the blood was a completely unexpected finding and is a complete game changer."
The blood-based liquid biopsy for detection of lymph node metastasis was described in the April 2, 2021, online edition of the journal Gastroenterology.
Related Links:
City of Hope
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Blood Test Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk and Reduces Need for Scans
- Unique Autoantibody Signature to Help Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis Years before Symptom Onset
- Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
- Low-Cost Point-Of-Care Diagnostic to Expand Access to STI Testing
- 18-Gene Urine Test for Prostate Cancer to Help Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Urine-Based Test Detects Head and Neck Cancer
- Blood-Based Test Detects and Monitors Aggressive Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Blood-Based Machine Learning Assay Noninvasively Detects Ovarian Cancer
- Simple PCR Assay Accurately Differentiates Between Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes
- Revolutionary T-Cell Analysis Approach Enables Cancer Early Detection
- Single Genetic Test to Accelerate Diagnoses for Rare Developmental Disorders
- Upgraded Syndromic Testing Analyzer Enables Remote Test Results Access
- Respiratory and Throat Infection PCR Test Detects Multiple Pathogens with Overlapping Symptoms
- Blood Circulating Nucleic Acid Enrichment Technique Enables Non-Invasive Liver Cancer Diagnosis
- First FDA-Approved Molecular Test to Screen Blood Donors for Malaria Could Improve Patient Safety
- Fluid Biomarker Test Detects Neurodegenerative Diseases Before Symptoms Appear
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
Mass spectrometry is a precise technique for identifying the chemical components of a sample and has significant potential for monitoring chronic illness health states, such as measuring hormone levels... Read more.jpg)
POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
Exosomes, tiny cellular bioparticles carrying a specific set of proteins, lipids, and genetic materials, play a crucial role in cell communication and hold promise for non-invasive diagnostics.... Read more
Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
The conventional methods for measuring free cortisol, the body's stress hormone, from blood or saliva are quite demanding and require sample processing. The most common method, therefore, involves collecting... Read moreHematology
view channel
Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
Hemoglobinopathies, the most widespread inherited conditions globally, affect about 7% of the population as carriers, with 2.7% of newborns being born with these conditions. The spectrum of clinical manifestations... Read more
First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
Arboviruses represent an emerging global health threat, exacerbated by climate change and increased international travel that is facilitating their spread across new regions. Chikungunya, dengue, West... Read more
POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Neutropenia, a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell crucial for fighting infections), is a frequent side effect of certain cancer treatments. This condition elevates the risk of infections,... Read more
First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
Hemoglobin disorders rank as some of the most prevalent monogenic diseases globally. Among various hemoglobin disorders, beta thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder, affects about 1.5% of the world's... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New CE-Marked Hepatitis Assays to Help Diagnose Infections Earlier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 354 million individuals globally are afflicted with chronic hepatitis B or C. These viruses are the leading causes of liver cirrhosis, liver... Read more
1 Hour, Direct-From-Blood Multiplex PCR Test Identifies 95% of Sepsis-Causing Pathogens
Sepsis contributes to one in every three hospital deaths in the US, and globally, septic shock carries a mortality rate of 30-40%. Diagnosing sepsis early is challenging due to its non-specific symptoms... Read morePathology
view channelAI-Powered Digital Imaging System to Revolutionize Cancer Diagnosis
The process of biopsy is important for confirming the presence of cancer. In the conventional histopathology technique, tissue is excised, sliced, stained, mounted on slides, and examined under a microscope... Read more
New Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Panel to Support Real-Time Surveillance and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Tuberculosis (TB), the leading cause of death from an infectious disease globally, is a contagious bacterial infection that primarily spreads through the coughing of patients with active pulmonary TB.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
While PCR tests are the gold standard of accuracy for virology testing, they come with limitations such as complexity, the need for skilled lab operators, and longer result times. They also require complex... Read more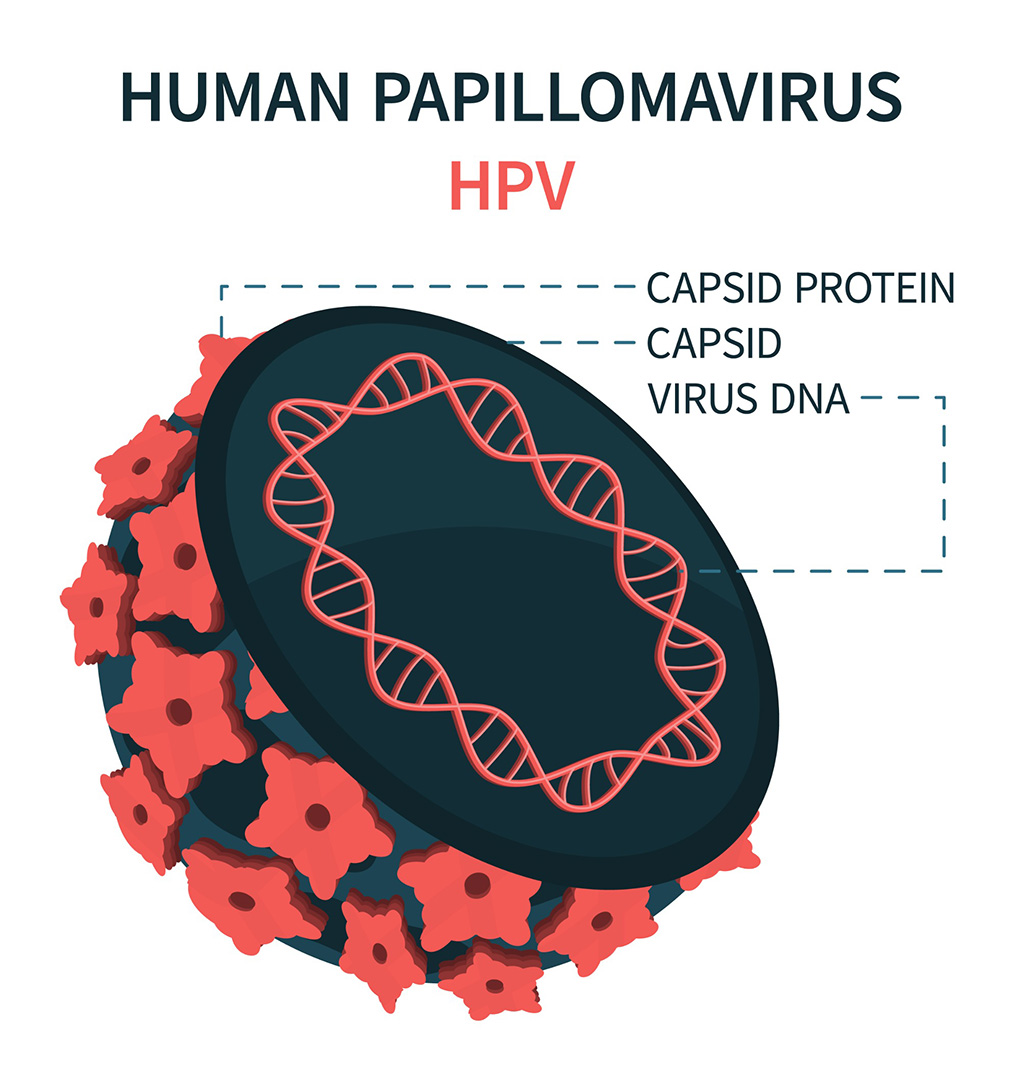
DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), recognized for its potential to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene, is a material that's increasingly catching the eye of the scientific community.... Read more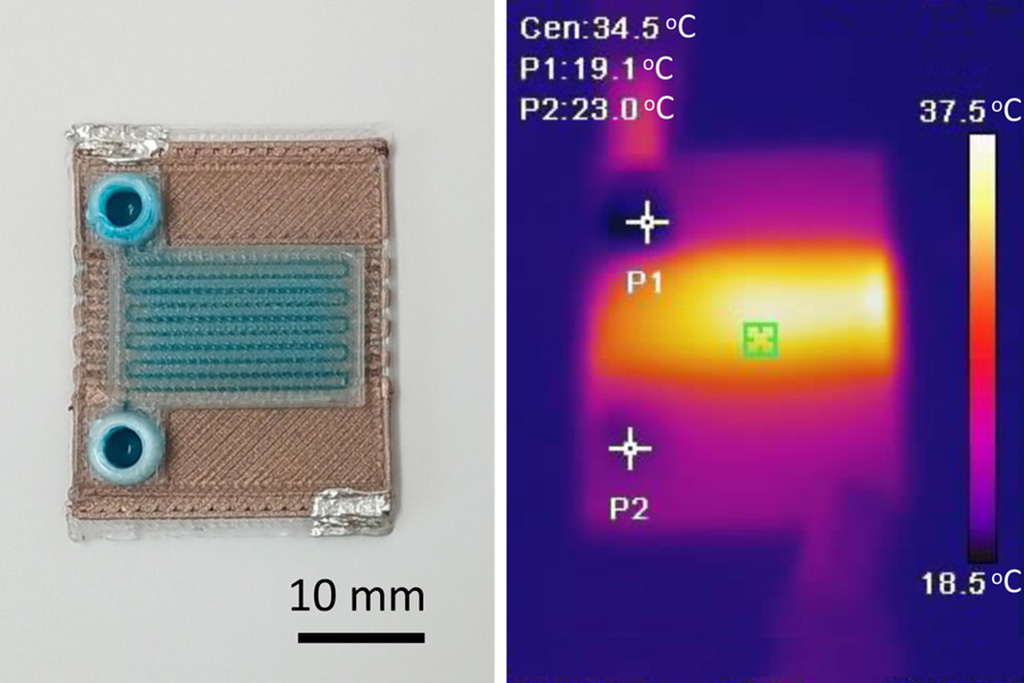
Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
Microfluidics, which are miniature devices that control the flow of liquids and facilitate chemical reactions, play a key role in disease detection from small samples of blood or other fluids.... Read more
Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
Home testing gained significant importance during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet the availability of rapid tests is limited, and most of them can only drive one liquid across the strip, leading to continued... Read moreIndustry
view channel
ECCMID Congress Name Changes to ESCMID Global
Over the last few years, the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID, Basel, Switzerland) has evolved remarkably. The society is now stronger and broader than ever before... Read more
Bosch and Randox Partner to Make Strategic Investment in Vivalytic Analysis Platform
Given the presence of so many diseases, determining whether a patient is presenting the symptoms of a simple cold, the flu, or something as severe as life-threatening meningitis is usually only possible... Read more
Siemens to Close Fast Track Diagnostics Business
Siemens Healthineers (Erlangen, Germany) has announced its intention to close its Fast Track Diagnostics unit, a small collection of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing products that is part of the... Read more












.jpg)