Two Simple Methods Prepare DNA Suitable For Digital PCR
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 19 Aug 2020 |
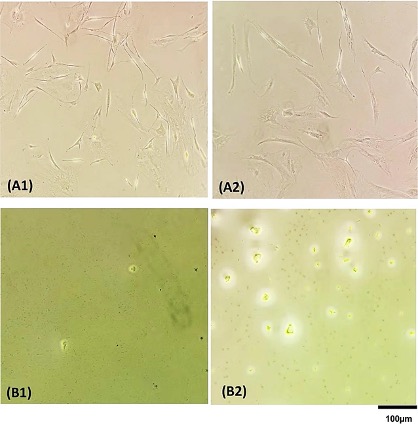
Cells in wells of a 96 well-plate before (A) and after (B) lysis cell by Direct PCR (B1) and Chelex100 (B2) (Photo courtesy of University Hospital Hamburg‐Eppendorf).
Although DNA of high quality can be easily prepared from cultured cells with commercially available kits, many studies involve a large number of samples which increases the cost drastically.
In addition, a limited amount of each sample is often a challenge, for example, for studies using cells of primary cultures for testing multiple drugs at multiple concentrations in multiple replicates, and studies or diagnosis involving defined subpopulations of human immune cells.
Medical scientists at the University Hospital Hamburg‐Eppendorf (Hamburg, Germany) used cells from a primary culture derived from a benign plexiform neurofibroma, a melanoma cell line, and a human fibroblast line. The cells were seeded into wells of 96‐well plates with at different concentrations, each in three replicates. The plates were incubated overnight for the cells to attach the cultural surface and subjected to DNA extraction on the next day after checking the adhesive living cells under a microscope.
After removing the medium, the wells were washed twice with PBS. Subsequently, 70 μL of the Direct PCR lysis reagent (PeqLab, Erlangen, Germany) supplemented with 0.2 mg/mL fresh proteinase K together with 70μL water was added to each well containing adhesive living cells. Supernatants containing the extracted DNA were further purified by precipitation. The team also lysed cells using chelex100 powder (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was carried out using 2 µL out of the 10 µL DNA and a primer pair for an exon of the NF1 gene which is used for the routine genetic diagnosis in their laboratory.
The investigators reported that for 1,000 cells from one primary culture and two tumor cell lines, DNA was reproducible and obtained with recovery rate (obtained/expected amount of DNA) in the range of 50%‐90% as measured by the fluorometer dyes instrument Qubit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). For digital PCR, more than 1,600 positive droplets were obtained for DNA from 1,000 cells using the Direct PCR method, corresponding to a yield efficiency of approximately 80%. Further reducing the number of cells down to 100 would be possible with 160 positive droplets expected. Both reagents are inexpensive at EUR 0.08/sample.
The authors concluded that the two methods were efficient; especially the Direct PCR reagent‐based method provides a simple and inexpensive method for preparing DNA suitable for digital PCR from small number of cells. The study was published on August 5, 2020 in the Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.
Related Links:
University Hospital Hamburg‐Eppendorf
PeqLab
Bio-Rad
Thermo Fisher Scientific
In addition, a limited amount of each sample is often a challenge, for example, for studies using cells of primary cultures for testing multiple drugs at multiple concentrations in multiple replicates, and studies or diagnosis involving defined subpopulations of human immune cells.
Medical scientists at the University Hospital Hamburg‐Eppendorf (Hamburg, Germany) used cells from a primary culture derived from a benign plexiform neurofibroma, a melanoma cell line, and a human fibroblast line. The cells were seeded into wells of 96‐well plates with at different concentrations, each in three replicates. The plates were incubated overnight for the cells to attach the cultural surface and subjected to DNA extraction on the next day after checking the adhesive living cells under a microscope.
After removing the medium, the wells were washed twice with PBS. Subsequently, 70 μL of the Direct PCR lysis reagent (PeqLab, Erlangen, Germany) supplemented with 0.2 mg/mL fresh proteinase K together with 70μL water was added to each well containing adhesive living cells. Supernatants containing the extracted DNA were further purified by precipitation. The team also lysed cells using chelex100 powder (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was carried out using 2 µL out of the 10 µL DNA and a primer pair for an exon of the NF1 gene which is used for the routine genetic diagnosis in their laboratory.
The investigators reported that for 1,000 cells from one primary culture and two tumor cell lines, DNA was reproducible and obtained with recovery rate (obtained/expected amount of DNA) in the range of 50%‐90% as measured by the fluorometer dyes instrument Qubit (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). For digital PCR, more than 1,600 positive droplets were obtained for DNA from 1,000 cells using the Direct PCR method, corresponding to a yield efficiency of approximately 80%. Further reducing the number of cells down to 100 would be possible with 160 positive droplets expected. Both reagents are inexpensive at EUR 0.08/sample.
The authors concluded that the two methods were efficient; especially the Direct PCR reagent‐based method provides a simple and inexpensive method for preparing DNA suitable for digital PCR from small number of cells. The study was published on August 5, 2020 in the Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.
Related Links:
University Hospital Hamburg‐Eppendorf
PeqLab
Bio-Rad
Thermo Fisher Scientific
Latest Molecular Diagnostics News
- Blood Test Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk and Reduces Need for Scans
- Unique Autoantibody Signature to Help Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis Years before Symptom Onset
- Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
- Low-Cost Point-Of-Care Diagnostic to Expand Access to STI Testing
- 18-Gene Urine Test for Prostate Cancer to Help Avoid Unnecessary Biopsies
- Urine-Based Test Detects Head and Neck Cancer
- Blood-Based Test Detects and Monitors Aggressive Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Blood-Based Machine Learning Assay Noninvasively Detects Ovarian Cancer
- Simple PCR Assay Accurately Differentiates Between Small Cell Lung Cancer Subtypes
- Revolutionary T-Cell Analysis Approach Enables Cancer Early Detection
- Single Genetic Test to Accelerate Diagnoses for Rare Developmental Disorders
- Upgraded Syndromic Testing Analyzer Enables Remote Test Results Access
- Respiratory and Throat Infection PCR Test Detects Multiple Pathogens with Overlapping Symptoms
- Blood Circulating Nucleic Acid Enrichment Technique Enables Non-Invasive Liver Cancer Diagnosis
- First FDA-Approved Molecular Test to Screen Blood Donors for Malaria Could Improve Patient Safety
- Fluid Biomarker Test Detects Neurodegenerative Diseases Before Symptoms Appear
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
Mass spectrometry is a precise technique for identifying the chemical components of a sample and has significant potential for monitoring chronic illness health states, such as measuring hormone levels... Read more.jpg)
POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
Exosomes, tiny cellular bioparticles carrying a specific set of proteins, lipids, and genetic materials, play a crucial role in cell communication and hold promise for non-invasive diagnostics.... Read more
Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
The conventional methods for measuring free cortisol, the body's stress hormone, from blood or saliva are quite demanding and require sample processing. The most common method, therefore, involves collecting... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk and Reduces Need for Scans
Lung cancer is extremely hard to detect early due to the limitations of current screening technologies, which are costly, sometimes inaccurate, and less commonly endorsed by healthcare professionals compared... Read more
Unique Autoantibody Signature to Help Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis Years before Symptom Onset
Autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) are thought to occur partly due to unusual immune responses to common infections. Early MS symptoms, including dizziness, spasms, and fatigue, often... Read more
Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is known to cause various cancers, including those of the genitals, anus, mouth, throat, and cervix. HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer (HPV+OPSCC) is the most common HPV-associated... Read moreHematology
view channel
Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
Hemoglobinopathies, the most widespread inherited conditions globally, affect about 7% of the population as carriers, with 2.7% of newborns being born with these conditions. The spectrum of clinical manifestations... Read more
First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
Arboviruses represent an emerging global health threat, exacerbated by climate change and increased international travel that is facilitating their spread across new regions. Chikungunya, dengue, West... Read more
POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Neutropenia, a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell crucial for fighting infections), is a frequent side effect of certain cancer treatments. This condition elevates the risk of infections,... Read more
First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
Hemoglobin disorders rank as some of the most prevalent monogenic diseases globally. Among various hemoglobin disorders, beta thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder, affects about 1.5% of the world's... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New CE-Marked Hepatitis Assays to Help Diagnose Infections Earlier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 354 million individuals globally are afflicted with chronic hepatitis B or C. These viruses are the leading causes of liver cirrhosis, liver... Read more
1 Hour, Direct-From-Blood Multiplex PCR Test Identifies 95% of Sepsis-Causing Pathogens
Sepsis contributes to one in every three hospital deaths in the US, and globally, septic shock carries a mortality rate of 30-40%. Diagnosing sepsis early is challenging due to its non-specific symptoms... Read morePathology
view channelAI-Powered Digital Imaging System to Revolutionize Cancer Diagnosis
The process of biopsy is important for confirming the presence of cancer. In the conventional histopathology technique, tissue is excised, sliced, stained, mounted on slides, and examined under a microscope... Read more
New Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Panel to Support Real-Time Surveillance and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Tuberculosis (TB), the leading cause of death from an infectious disease globally, is a contagious bacterial infection that primarily spreads through the coughing of patients with active pulmonary TB.... Read moreIndustry
view channel
ECCMID Congress Name Changes to ESCMID Global
Over the last few years, the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID, Basel, Switzerland) has evolved remarkably. The society is now stronger and broader than ever before... Read more
Bosch and Randox Partner to Make Strategic Investment in Vivalytic Analysis Platform
Given the presence of so many diseases, determining whether a patient is presenting the symptoms of a simple cold, the flu, or something as severe as life-threatening meningitis is usually only possible... Read more
Siemens to Close Fast Track Diagnostics Business
Siemens Healthineers (Erlangen, Germany) has announced its intention to close its Fast Track Diagnostics unit, a small collection of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing products that is part of the... Read more













.jpg)