专家建议减少住院患者的检验次数
|
By LabMedica International staff writers Posted on 21 Dec 2017 |
图像:收集人血样做检验;过多的检验可能引起医院获得性贫血(图片蒙Rebecca Zeffert惠赐)。
住院患者的日常化验反映了临床业务的浪费,它威胁着医疗护理的价值。大量职业社团主张把以临床稳定性为名的重复化验认定为无价值医疗。
过多的静脉切开术可能导致医院获得性贫血,增加开支,引起不必要的下游检验和手术。努力降低化验频度会提高病人满意度,减少成本,且不会对病人预后造成不良影响。
美国马里兰州巴尔的摩市约翰霍普金斯大学医学院的内科医师与北美其它几家单位的专家编制并草拟了一份基于经验的质量改进计划,以减少住院患者的重复化验。作者引用的各项研究都显示,一线医疗工作者化验的请求量减少了8%到19%,作者报告说,每年节省的费用范围是60万美元到200万美元。
专家建议,有必要设计以数据为支撑的全医院培训计划,共同勾勒和标准化最佳实践。确立要减少的化验请求的数量目标,向送检医师提供即时反馈,显示他们个人送检的模式,他们因此能意识到自己的行为不符合已得到一致认可的标准。也可以修改用于请求化验的电子系统的程序,限制“预订”化验的数量,同时留意是否有更好的送检原因,而不是机械地天天送检。
迄今已在多家机构部署了大量干预措施,但没有一个标准方法。医疗工作者和行政领导应该仔细制定行动策略,并优化工作方式,以减少每天的化验次数。已发表的论文显示,减少重复的日常化验不会导致漏诊或增加再次入院的数量。
该研究的论文发表于2017年10月16日的《JAMA》杂志《内科》分册。领衔作者、第三年的内科住院医师Kevin P. Eaton博士说:“抽血次数过多可能耗尽病人的血红蛋白,这又经常导致重复化验。有人估计近20%的住院患者会得中度到重度的医院获得性贫血。如此反复会给病人带来更多不必要的检验、干预和花销。”
Related Links:
约翰霍普金斯大学医学院
过多的静脉切开术可能导致医院获得性贫血,增加开支,引起不必要的下游检验和手术。努力降低化验频度会提高病人满意度,减少成本,且不会对病人预后造成不良影响。
美国马里兰州巴尔的摩市约翰霍普金斯大学医学院的内科医师与北美其它几家单位的专家编制并草拟了一份基于经验的质量改进计划,以减少住院患者的重复化验。作者引用的各项研究都显示,一线医疗工作者化验的请求量减少了8%到19%,作者报告说,每年节省的费用范围是60万美元到200万美元。
专家建议,有必要设计以数据为支撑的全医院培训计划,共同勾勒和标准化最佳实践。确立要减少的化验请求的数量目标,向送检医师提供即时反馈,显示他们个人送检的模式,他们因此能意识到自己的行为不符合已得到一致认可的标准。也可以修改用于请求化验的电子系统的程序,限制“预订”化验的数量,同时留意是否有更好的送检原因,而不是机械地天天送检。
迄今已在多家机构部署了大量干预措施,但没有一个标准方法。医疗工作者和行政领导应该仔细制定行动策略,并优化工作方式,以减少每天的化验次数。已发表的论文显示,减少重复的日常化验不会导致漏诊或增加再次入院的数量。
该研究的论文发表于2017年10月16日的《JAMA》杂志《内科》分册。领衔作者、第三年的内科住院医师Kevin P. Eaton博士说:“抽血次数过多可能耗尽病人的血红蛋白,这又经常导致重复化验。有人估计近20%的住院患者会得中度到重度的医院获得性贫血。如此反复会给病人带来更多不必要的检验、干预和花销。”
Related Links:
约翰霍普金斯大学医学院
Latest 血液学 News
Channels
Clinical Chemistry
view channel
3D Printed Point-Of-Care Mass Spectrometer Outperforms State-Of-The-Art Models
Mass spectrometry is a precise technique for identifying the chemical components of a sample and has significant potential for monitoring chronic illness health states, such as measuring hormone levels... Read more.jpg)
POC Biomedical Test Spins Water Droplet Using Sound Waves for Cancer Detection
Exosomes, tiny cellular bioparticles carrying a specific set of proteins, lipids, and genetic materials, play a crucial role in cell communication and hold promise for non-invasive diagnostics.... Read more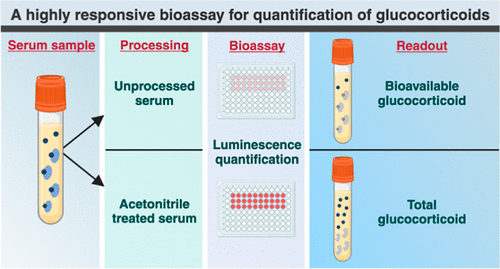
Highly Reliable Cell-Based Assay Enables Accurate Diagnosis of Endocrine Diseases
The conventional methods for measuring free cortisol, the body's stress hormone, from blood or saliva are quite demanding and require sample processing. The most common method, therefore, involves collecting... Read moreMolecular Diagnostics
view channel
Blood Test Accurately Predicts Lung Cancer Risk and Reduces Need for Scans
Lung cancer is extremely hard to detect early due to the limitations of current screening technologies, which are costly, sometimes inaccurate, and less commonly endorsed by healthcare professionals compared... Read more
Unique Autoantibody Signature to Help Diagnose Multiple Sclerosis Years before Symptom Onset
Autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis (MS) are thought to occur partly due to unusual immune responses to common infections. Early MS symptoms, including dizziness, spasms, and fatigue, often... Read more
Blood Test Could Detect HPV-Associated Cancers 10 Years before Clinical Diagnosis
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is known to cause various cancers, including those of the genitals, anus, mouth, throat, and cervix. HPV-associated oropharyngeal cancer (HPV+OPSCC) is the most common HPV-associated... Read moreHematology
view channel
Next Generation Instrument Screens for Hemoglobin Disorders in Newborns
Hemoglobinopathies, the most widespread inherited conditions globally, affect about 7% of the population as carriers, with 2.7% of newborns being born with these conditions. The spectrum of clinical manifestations... Read more
First 4-in-1 Nucleic Acid Test for Arbovirus Screening to Reduce Risk of Transfusion-Transmitted Infections
Arboviruses represent an emerging global health threat, exacerbated by climate change and increased international travel that is facilitating their spread across new regions. Chikungunya, dengue, West... Read more
POC Finger-Prick Blood Test Determines Risk of Neutropenic Sepsis in Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy
Neutropenia, a decrease in neutrophils (a type of white blood cell crucial for fighting infections), is a frequent side effect of certain cancer treatments. This condition elevates the risk of infections,... Read more
First Affordable and Rapid Test for Beta Thalassemia Demonstrates 99% Diagnostic Accuracy
Hemoglobin disorders rank as some of the most prevalent monogenic diseases globally. Among various hemoglobin disorders, beta thalassemia, a hereditary blood disorder, affects about 1.5% of the world's... Read moreImmunology
view channel
Diagnostic Blood Test for Cellular Rejection after Organ Transplant Could Replace Surgical Biopsies
Transplanted organs constantly face the risk of being rejected by the recipient's immune system which differentiates self from non-self using T cells and B cells. T cells are commonly associated with acute... Read more
AI Tool Precisely Matches Cancer Drugs to Patients Using Information from Each Tumor Cell
Current strategies for matching cancer patients with specific treatments often depend on bulk sequencing of tumor DNA and RNA, which provides an average profile from all cells within a tumor sample.... Read more
Genetic Testing Combined With Personalized Drug Screening On Tumor Samples to Revolutionize Cancer Treatment
Cancer treatment typically adheres to a standard of care—established, statistically validated regimens that are effective for the majority of patients. However, the disease’s inherent variability means... Read moreMicrobiology
view channel
New CE-Marked Hepatitis Assays to Help Diagnose Infections Earlier
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), an estimated 354 million individuals globally are afflicted with chronic hepatitis B or C. These viruses are the leading causes of liver cirrhosis, liver... Read more
1 Hour, Direct-From-Blood Multiplex PCR Test Identifies 95% of Sepsis-Causing Pathogens
Sepsis contributes to one in every three hospital deaths in the US, and globally, septic shock carries a mortality rate of 30-40%. Diagnosing sepsis early is challenging due to its non-specific symptoms... Read morePathology
view channelAI-Powered Digital Imaging System to Revolutionize Cancer Diagnosis
The process of biopsy is important for confirming the presence of cancer. In the conventional histopathology technique, tissue is excised, sliced, stained, mounted on slides, and examined under a microscope... Read more
New Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Panel to Support Real-Time Surveillance and Combat Antimicrobial Resistance
Tuberculosis (TB), the leading cause of death from an infectious disease globally, is a contagious bacterial infection that primarily spreads through the coughing of patients with active pulmonary TB.... Read moreTechnology
view channel
New Diagnostic System Achieves PCR Testing Accuracy
While PCR tests are the gold standard of accuracy for virology testing, they come with limitations such as complexity, the need for skilled lab operators, and longer result times. They also require complex... Read more
DNA Biosensor Enables Early Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2), recognized for its potential to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene, is a material that's increasingly catching the eye of the scientific community.... Read more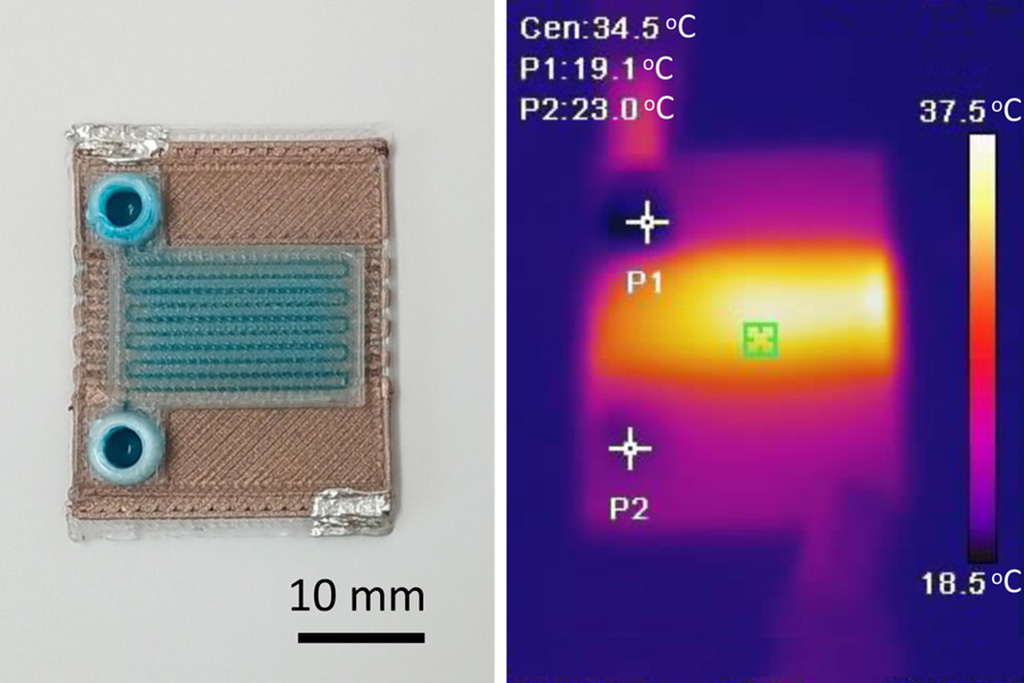
Self-Heating Microfluidic Devices Can Detect Diseases in Tiny Blood or Fluid Samples
Microfluidics, which are miniature devices that control the flow of liquids and facilitate chemical reactions, play a key role in disease detection from small samples of blood or other fluids.... Read more
Breakthrough in Diagnostic Technology Could Make On-The-Spot Testing Widely Accessible
Home testing gained significant importance during the COVID-19 pandemic, yet the availability of rapid tests is limited, and most of them can only drive one liquid across the strip, leading to continued... Read moreIndustry
view channel
ECCMID Congress Name Changes to ESCMID Global
Over the last few years, the European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases (ESCMID, Basel, Switzerland) has evolved remarkably. The society is now stronger and broader than ever before... Read more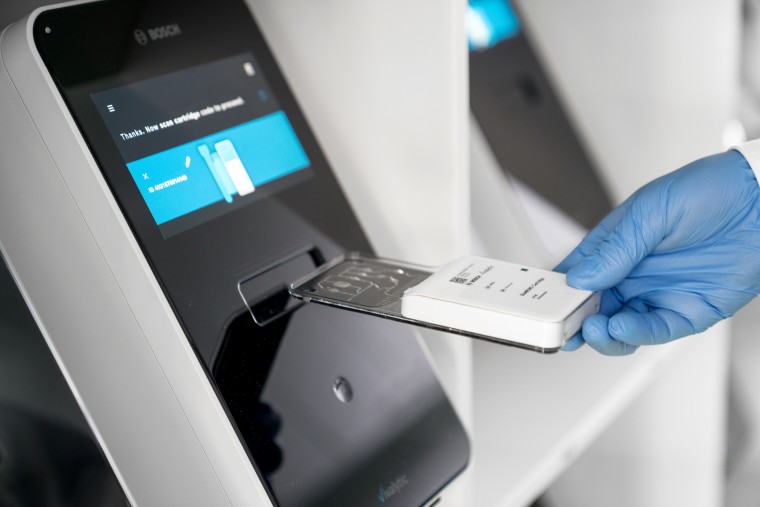
Bosch and Randox Partner to Make Strategic Investment in Vivalytic Analysis Platform
Given the presence of so many diseases, determining whether a patient is presenting the symptoms of a simple cold, the flu, or something as severe as life-threatening meningitis is usually only possible... Read more
Siemens to Close Fast Track Diagnostics Business
Siemens Healthineers (Erlangen, Germany) has announced its intention to close its Fast Track Diagnostics unit, a small collection of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing products that is part of the... Read more













.jpg)