Cord Blood Outperforms Matched Donor in Bone Marrow Transplants
By LabMedica International staff writers
Posted on 08 Aug 2016
A common treatment for blood cancers is to erase a patient's leukemic blood system and then regrow a new blood system using donor blood stem cells. The closer the match between donor cells and a patient's blood system, the less chance the new blood system will attack the patient's tissues which reduces the chance of graft - versus - host disease.Posted on 08 Aug 2016
There are four possible sources of donor cells: a matched, related donor, commonly a close family member, a matched, unrelated donor from a database of 25 million people who have agreed to donate, umbilical cord blood from a bank of stored samples, and haploidentical transplant which is a promising technique requiring only a half match with a related donor.
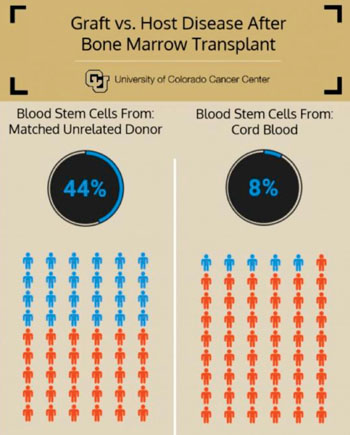
Image: Reduced chronic graft-versus-host disease with cord blood, compared with blood from unrelated matched donor, three years after bone marrow transplant (Photo courtesy of the University of Colorado Cancer Center).
Scientists at the University of Colorado Denver (Aurora, CO, USA) compared 51 consecutive patients receiving umbilical cord blood transplants (CBT) with 57 consecutive patients receiving matched, unrelated donors (MUD). The incidence of severe chronic graft-versus-host disease was 44% in patients who had received transplants from MUD and 8% in patients who had received CBT.
At three years post-transplant, in addition to other difference in severe chronic graft-versus-host disease (cGVHD), overall rates of cGVHD were 68% following MUD and 32% following CBT. Again at three years, patients receiving CBT had been off immunosuppression since a median 268 days from transplant; patients receiving MUD had not ceased immunosuppression to a degree that allowed scientists to determine the median.
Jonathan Gutman, MD, the senior investigator and lead author, said, “When you do an allogeneic transplant, when someone else is the donor, the new blood system has the potential to attack the patient. This is graft-versus-host disease, which can be debilitating and even fatal. Our results show that, long term, receiving a cord blood transplant is less likely than receiving a transplant from an unrelated, matched donor to result in graft-versus-host disease. As a result, we have chosen to use cord blood as our first choice in cases where a matched, related donor is unavailable.” The study was published on July 11, 2016, in the journal Bone Marrow Transplantation.
Related Links:
University of Colorado Denver













